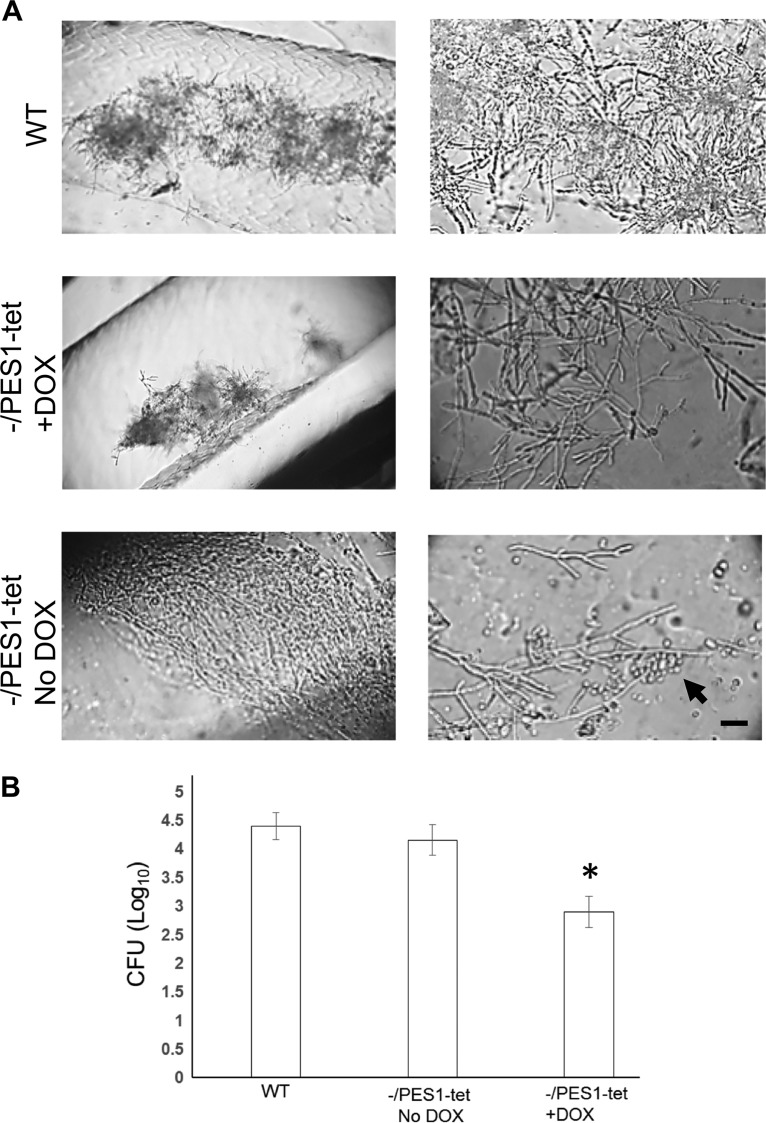
FIG 7 .
Biofilm formation and dispersal in jugular vein-catheterized mice. (A) Germinating C. albicans tetracycline-regulatable PES1 strain pes1/PES1-tet grown in YNB medium with and without doxycycline was instilled in the lumen of the catheters (full catheter volume) at a concentration of 5 × 106 cells/ml. Biofilms were allowed to develop for 3 days, after which the catheters were harvested, cut laterally, and examined under a phase-contrast microscope. While all 3 strains developed biofilms in the catheters in the presence or absence of DOX, the Pes1-tet hyphae displayed increased lateral yeast production in the absence of DOX (arrow). Bar, 20 µm. (B) The extent of biofilm-mediated dissemination in mice harboring the catheters containing the two strains was also determined by measuring CFU levels in the kidney. In the presence of DOX, dissemination and kidney colonization were reduced significantly (15-fold). *, P < 0.01 (compared to the mice with catheters infected with the wild-type strain or with Pes1-tet without DOX).