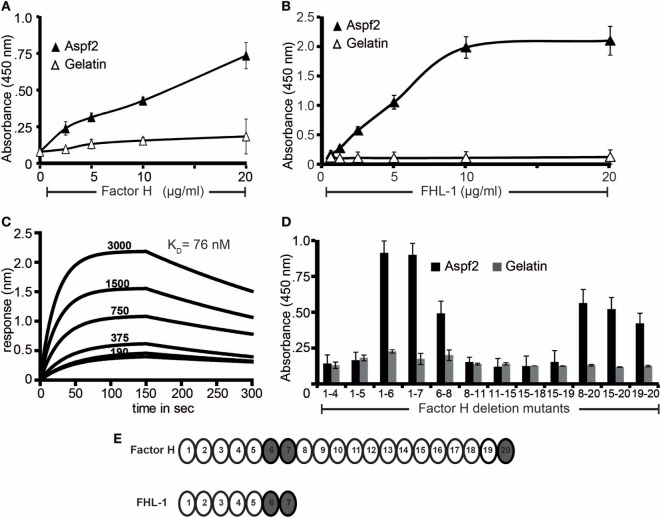
Figure 1.
Recombinant Aspf2 binds to Factor H and factor-H-like protein 1 (FHL-1). (A) Aspf2 binds to Factor H dose-dependently. Aspf2 binding to Factor H was assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Factor H was immobilized onto a microtiter plate, and Aspf2 at the indicated amounts was added. After washing, bound Aspf2 was detected with mAb Aspf2. Aspf2 did not bind to gelatin. (B) Aspf2 binds to FHL-1 dose-dependently. Aspf2 at increasing amounts was added to immobilized FHL-1, and bound Aspf2 was detected by with mAb Aspf2. Aspf2 did not bind to gelatin. (C) Factor H binds to Aspf2 with high affinity. The binding affinity of Factor H to Aspf2 was evaluated by biolayer interferometry. Aspf2 was coupled to the surface of NTA biosensors, and Factor H at 190, 375, 750, 1,500, and 3,000 nM concentrations was added as analyte. For each concentration, the association of complex was assessed for 150 s, and the dissociation was evaluated for 150 s. Factor H binds to Aspf2 with a KD of 76 nM. Heat-inactivated (95°C) Factor H did not bind to Aspf2 (bottom line) (D) Mapping of Aspf2-binding regions within Factor H and FHL-1. Binding of Aspf2 to the indicated Factor H/FHL-1 deletion mutants was investigated by ELISA. Aspf2 was added to immobilized Factor H/FHL-1 deletion mutants, and bound Aspf2 was detected by mouse Aspf2 anti-serum. Aspf2 binds to Factor H via SCR6–7 and SCR20 and to FHL-1 through SCR6–7. (E) The structure of Factor H and FHL-1 are shown with their corresponding domains short consensus repeats (SCR). Aspf2-binding domains are highlighted in brown. Panels A, B, and D represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments.