Figure 2.
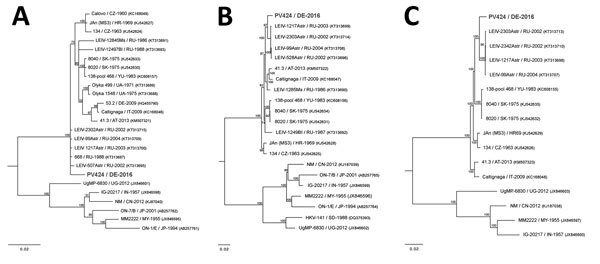
Bayesian phylogeny trees based on full-genome coding region sequences of small, medium, and large RNA segments of Batai virus and comparison viruses. A) Small RNA segments (69–770 bp). Bunyamwera virus (GenBank accession no. D00353) was used as the outgroup. B) Medium RNA segments (42–4,346 bp). Bunyamwera virus (GenBank accession no. M11852) was used as the outgroup. C) Large RNA segments (49–6,762 bp). Bunyamwera virus (GenBank accession no. X14383) was used as the outgroup. Bold indicates virus isolated in this study. Analysis was performed for 1 million generations and sampled every 100 steps. The first 25% of samples were discarded as burn-in according to MrBayes (11). Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano nucleotide substitution model was selected as best-fit model according to Bayesian information criteria. Numbers at the nodes indicate posterior probabilities percentage. GenBank accession numbers are provided for comparison isolates; accession nos. of the isolated Batai virus strain PV424/DE-2016 are small, MH299972; medium, MH299973; large, MH299974. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
