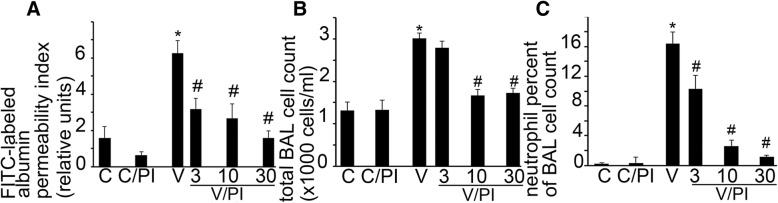
Fig. 4.
PERK inhibition reduces VILI in vivo. PERK. Rats were pretreated with increasing dosease of 3, 10 or 30 mg/kg GSK2606414 compound (PI) or its vehicle (0.1% TWEEN 80 in 0.5% hydroxyethyl-methylcellulose) via oral gavage. Four hours later the animals were anesthetized and mechanically ventilated (V) with 20 ml/kg tidal volume without postive end expiratory pressure or allowed to breathe spontaneously (c). Lung injury indices were compared among all groups. a PI treatment (V/PI) improved mechanical stretch-induced alveolo-capillary barrier dysfunction in a dose-dependent fashion. Lung injury parameters were not affected by PI in controls (C/PI). V/PI animals showed decreased fluorescent isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled albumin permeability index when compared to V. b-c Mechanical stretch significantly increased BAL total and neutrophil cell count. Animals treated per V/PI protocol exhibited reduced infiltrating cell numbers when compared to V. Statistics: Kruskal-Wallis test was performed for multiple group comparison, and intergroup differences were analyzed with Wilcoxon rank sum test. N = 5–9 animals/condition. Data is presented as averaged values ±SEM.*represents significant increase in V vs. C conditions and #represents significant decrease in VPI vs. V conditions, p < 0.05