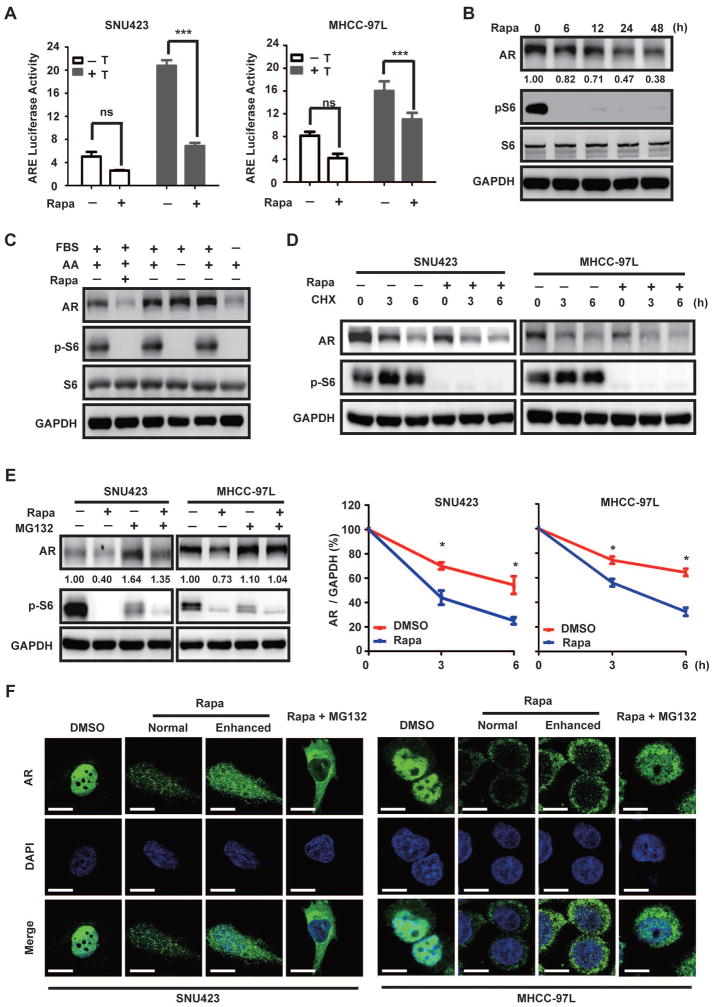
Fig. 5. mTOR promotes AR transcriptional activity by enhancing AR stability and nuclear localization.
(A) Rapamycin suppresses AR transcriptional activity in HCC. The activity of ARE luciferase reporter was assayed in the absence or presence of rapamycin without or with testosterone for 24 h in SNU423 and MHCC9-7L cells. Luciferase activity is expressed relative to the Renilla control. Data (mean ± SD, n = 3) were analyzed by Student’s T test; *** p < 0.001.
(B) Rapamycin decreases AR protein level. SNU423 cells were treated with rapamycin for different times and measured for AR protein by immunoblot. Numbers represent relative quantification of AR protein (representative of three independent experiments, arbitrary unit).
(C) AR protein level is regulated by growth factors, not amino acids. SNU423 cells were starved from serum or amino acids for 24 h and analyzed for AR protein level by immunoblot.
(D) Rapamycin accelerates AR protein turnover. SNU423 and MHCC-97L cells were treated with or without rapamycin in the presence of cycloheximide (CHX). The ratio of AR/GAPDH is used to calculate AR stability. Lower panel shows quantification of the results. Data (mean ± SD, n = 4) were analyzed by Student’s T test; *p < 0.05.
(E) Rapamycin induces proteasome-dependent AR degradation. SNU423 and MHCC-97L cells were treated without or with rapamycin in the presence of the proteasome inhibitor MG132. The numbers show the relative AR protein amount representative of three independent experiments.
(F) Rapamycin inhibits AR nuclear localization in HCC cells. SNU423 and MHCC-97L cells were treated without or with rapamycin for 24 h. AR localization was analyzed by IF and the nuclei were counterstained by DAPI. Scar bar 10 μm. Normal, normal exposure; Enhanced, images were enhanced to show details.