Fig. 6. Correction model.
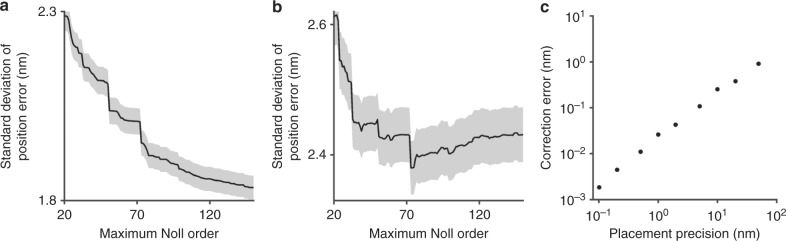
a–b Plots showing representative values of the standard deviation of position errors in a single lateral dimension after correction, as a function of the number of consecutive Zernike polynomials in the model, or the maximum Noll order. A maximum Noll order of less than 20 corrects the largest fraction of the position errors. a At the center of the standard array from which we derive the model, the standard deviation decreases monotonically with maximum Noll order as the model corrects position errors due primarily to aberrations. b After applying the model from (a) to a different region of the standard array, the standard deviation decreases to a minimum at a maximum Noll order of 73 and then increases with additional orders, indicating erroneous inclusion of position errors due to placement precision at the array center. Plots for other regions of the array are similar. Gray bounds are one standard error. c Plot showing correction error, which increases approximately linearly with placement precision. Standard errors are smaller than the data markers