Fig. 2.
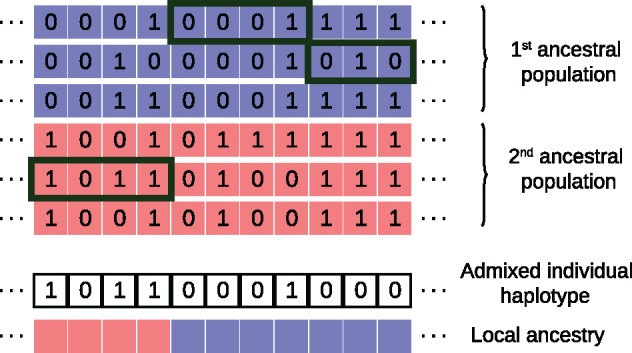
Graphical description of Local Ancestry Inference as implemented in the software Loter. Given a collection of parental haplotypes from the source populations depicted in blue and red, Loter assumes that an haplotype of an admixed individuals is modeled as a mosaic of existing parental haplotypes. In this example, the first term of equation (1) (loss function) is equal to 1 because of a single mismatch between parental and admixed haplotype located at the next-to-last position, and the second term of equation (1) (regularization term) is equal to 2λ because there are two switches between parental haplotypes. The displayed solution corresponds to the mathematical solution where haplotypes are numbered from top to bottom, and sj = k if the admixed haplotype results from a copy of the kth parental haplotype at the jth SNP.
