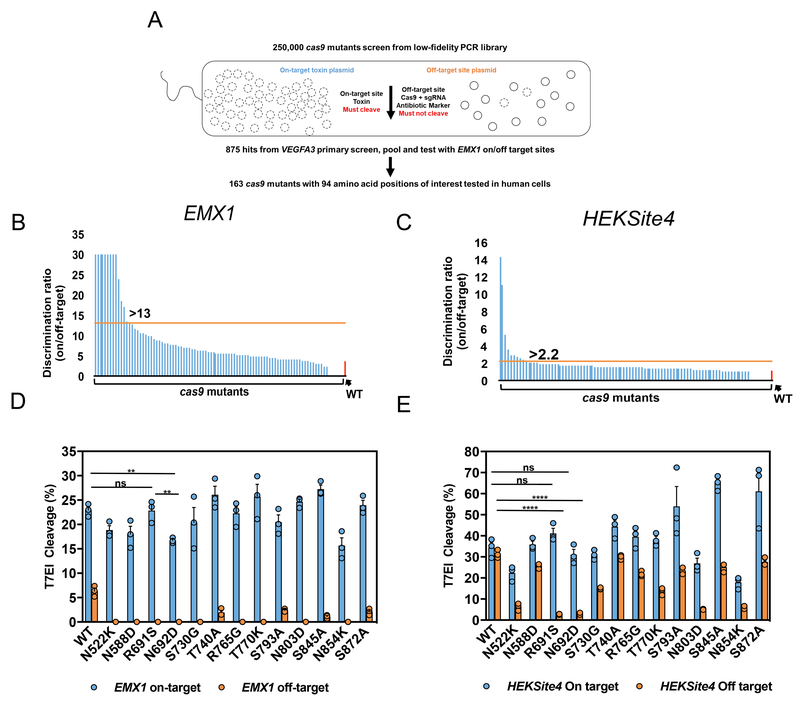
Figure 2. Unbiased bacterial selection for cas9 mutants that reduce off-target editing and maintain on-target potency.
(a) A general schematic for the bacterial selection scheme to isolate cas9 mutants with reduced off-target editing and high on-target activity. Approximately 250,000 clones were screened for cleavage of the on-target VEGFA3 toxin plasmid, and avoidance of cleavage of the off-target plasmid. We isolated 875 surviving colonies from the primary screen, and pooled surviving plasmids were screened a second time using EMX1 guide and target sites. Ultimately 163 cas9 mutant plasmids were sequenced with mutations at 94 positions occurring twice or more. (b,c) Discrimination ratio (on/off-target editing efficiency) of WT Cas9 (red bar) and all 94 cas9 point mutations (blue bars) delivered by plasmid into HEK293 cells with the EXM1 (b) or HEKSite4 (c) gRNAs (2-part). Horizontal lines (orange) indicate the minimum discrimination ratios (indicated numerically above bars) used to select mutants for further testing. Mutants that maintained greater than 50% on-target editing and reduced off-target editing beyond the limits of detection were arbitrarily set at 30 (EMX1 only) to indicate that they were carried forward into subsequent screening steps. (d,e) On- and off-target editing efficiency facilitated by WT and mutant Cas9 plasmids from Fig. 2b,c examined with crRNAs that target the EMX1 (d) and HEKSite4 (e) delivered as by lipofection into HEK293 cells. The on-target site “ON” (blue – left Y-axis) and off-target site “OFF” (orange – right Y-axis) for each guide are indicated and sequence maps are listed in Fig. 1b. Bars represent mean ± s.e.m., n=9 independent experiments performed at different times. **P<0.01, ****P < 0.0001, NS (not significant) = P ≥ 0.05, two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.