Figure 1.
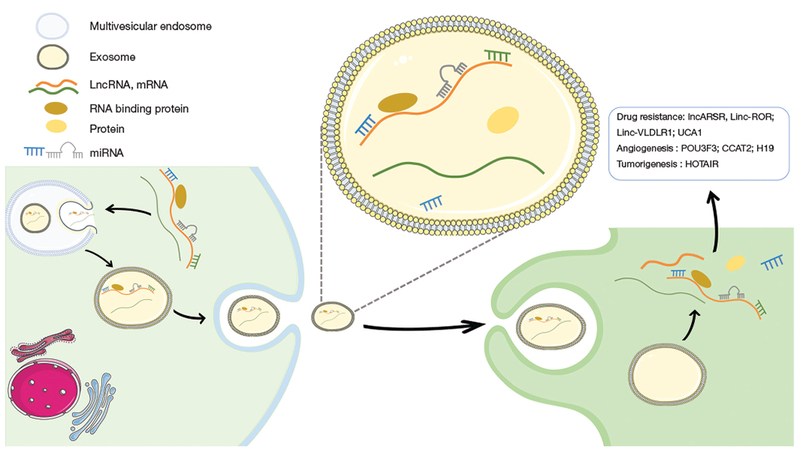
Intercellular communication via exosomal lncRNAs. Cancer cells use exosomal lncRNAs to modify the characteristics of neighboring cells. Recent studies show that functional lncRNAs encapsulated in exosomes are secreted by neoplastic cells in various bodily fluids. The exosomal lncRNAs are internalized by different types of recipient cells and this event leads to phenotypical changes. The role of exosomal lncRNAs is not completely deciphered. To date we know that exosomal lncRNAs can promote angiogenesis in neighboring endothelial cells, transmit tumor drag resistant phenotypes and stimulate tumor growth. This data makes lncRNAs appealing therapeutic targets that can enhance the chemosensitivity of tumor cells or inhibit neovascularization. The exosome can be also perceived as a cocktail of molecules (lncRNAs, mRNAs, microRNAs, proteins) that reach high concentration and could co-interact. lncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs.
