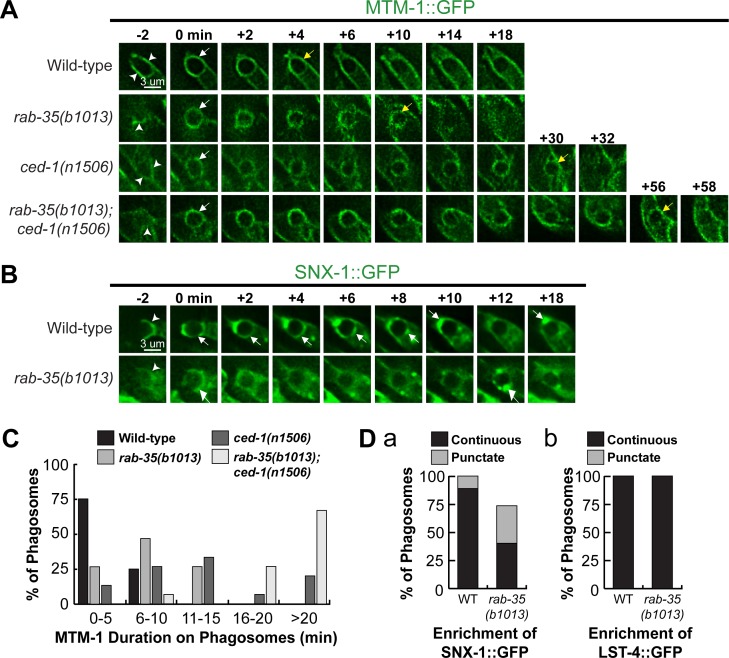
Fig 7. The rab-35(b1013) mutation impairs MTM-1 removal from, and SNX-1 recruitment to, phagosomal surfaces.
(A and B) Time-lapse images during and after the formation of a phagosome carrying C3 in embryos of different genotypes expressing Pced-1 mtm-1::gfp (A) or Pced-1 snx-1::gfp (B), respectively. “0 min” is the moment when a phagosome is just formed. Arrowheads indicate extending pseudopods. White and yellow arrows on phagosomes in (A) indicate the time points when MTM-1::GFP first and last appear on the phagosome surface, respectively. White arrows in (B) mark the regions on the phagosomal surface that have an enriched GFP signal. (C) Histogram displaying the range of time that MTM-1 persists on phagosomes in wild-type and rab-35(b1013) embryos. Phagosomes bearing cell corpses C1, C2, and C3 were scored. This time interval is defined as that between the “0 min” time point and the first time point that MTM-1 is no longer found on the phagosome. For each genotype, at least 15 phagosomes were scored. (D) The efficiency of recruitment of SNX-1::GFP (a) and LST-4::GFP (b) to the surface of phagosomes carrying C1, C2, and C3 was scored in various genotypes. SNX-1::GFP is either distributed onto the entire phagosomal surface evenly (“continuous”) or attached to phagosomal surfaces as puncta (“punctate”) (a), whereas LST-4::GFP is enriched onto phagosomes only in the “continuous” pattern (b). For each genotype, at least 15 phagosomes were scored.