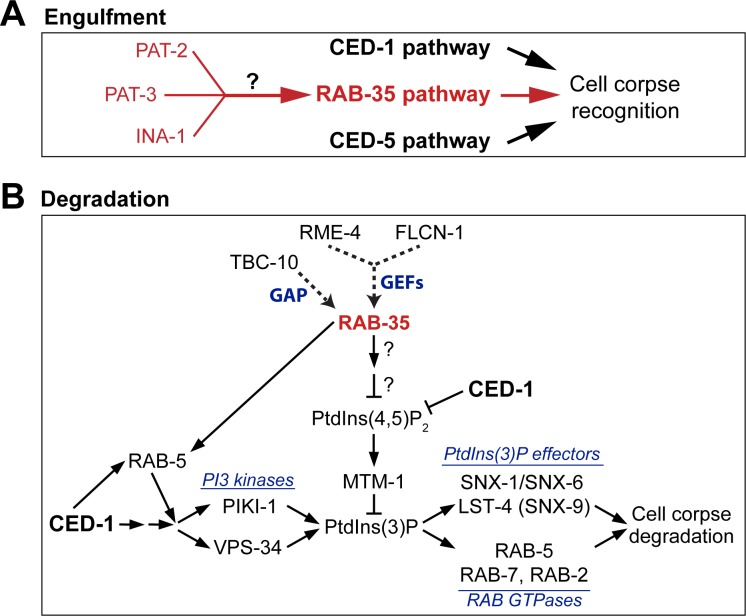
Fig 11. Model explaining RAB-35’s action in the clearance of apoptotic cells.
Diagram illustrating the roles of RAB-35 in the engulfment (A) and degradation (B) of cell corpses in C. elegans. See Discussion for more details. RAB-35 functions in parallel with the ced-1/-6/-7/dyn-1 and ced-2/-5/-10/-12 pathways in the recognition of cell corpses but in the same pathway as ina-1, pat-2, and pat-3 (A). In addition, RAB-35 functions in parallel to the CED-1 pathway during phagosome maturation (B). On the surface of nascent phagosomes, RAB-35 stimulates the turnover of both PtdIns(4,5)P2 and its effector MTM-1, a PI-3 phosphatase, on the phagosomal surfaces. In addition, RAB-35 helps to recruit RAB-5, which promotes the production of PtdIns(3)P. Together, these two events promote the production of phagosomal PtdIns(3)P. PtdIns(3)P in turn promotes the recruitment of its downstream effectors, driving the progression of phagosome maturation and cell corpse degradation. rab-35 mutants are defective in the recruitment of SNX-1 but not LST-4/SNX-9 to phagosomes, perhaps due to that other factors may be involved in their recruitment. Question marks indicate that how RAB-35 regulates PtdIns(4,5)P2 turnover remains to be investigated.