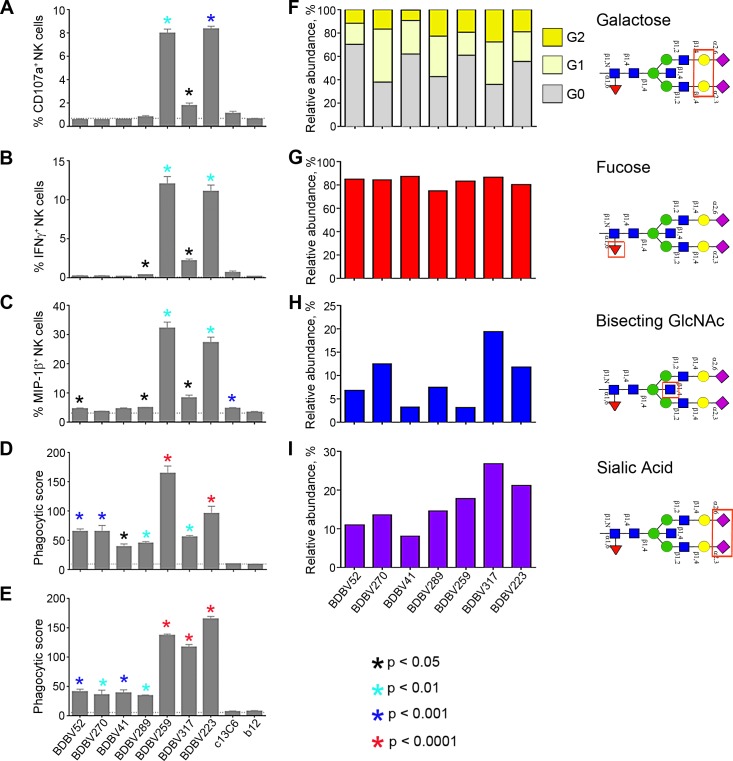
Fig 5. Stalk-specific, but not glycan cap-specific mAbs, induce high antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and phagocytosis.
A-C, expression of NK cell activation markers CD107A (A), IFNγ (B), MIP-1β (C), and phagocytic activity of THP-1 monocytes (D) or neutrophils (E) in response to incubation with BDBV GP immune complexes. Bars show mean values of triplicates ± SE from a single NK cell donor and are representative of two independent experiments across four NK cell donors (A-C), or mean values of duplicates ± SE, and are representative of two independent experiments (D, E). P values were calculated by factorial ANOVA (Fisher LSD test), compared to the irrelevant mAb b12, which is a HIV-specific human IgG1. The EBOV GP-specific mAb, c13C6 (IgG1), was included as a specificity control. F-I, analysis of glycan content in the Fc fragments of mAbs: the relative abundance of galactose (F), fucose (G), bisecting N-acetylglucosamine (H), or sialic acid (I). Bars show fraction of specific carbohydrate residue-containing molecules in a total antibody pool. Schematic structures of N297-associated bi-antennary glycan with analyzed sugar moieties highlighted with rectangles are indicated at the right.