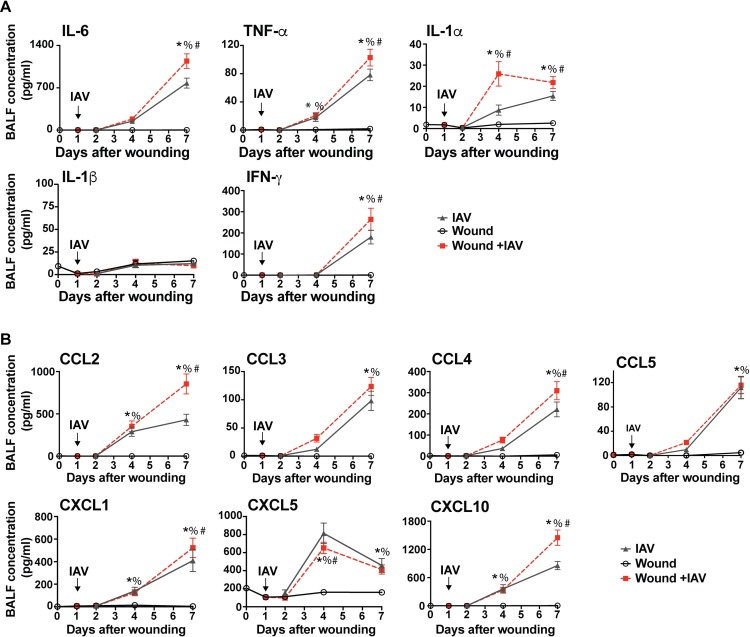
Fig 4. There is an increase in inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the BALF of mice that are wounded and infected with IAV compared to wounding or IAV infection alone.
Mice were wounded by PVA sponge implantation alone, infected with IAV alone, or wounded and IAV-infected 24 hours later. Control mice were unwounded and uninfected (wounding day 0). BALF levels of chemokines and cytokines were measured days 0, 1, 2, 4, and 7 after wounding. The inflammatory cytokines IL-6, TNFα, IL-1α, IL-β, and IFNγ were detected in the BALF (A). The chemokines CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CXCL1, CXCL5, and CXCL10 were detected in BALF (B). The data shown are cumulative from at least 3 independent experiments with n = 12 (on all groups except d7 where n = 18). The mean values are displayed with SEM. To compare 3 or more groups the Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance was used. Results are considered statistically significant when the P value ≤ 0.05. Statistically significant changes between control (wounding day 0) and wound + IAV are denoted by %, between IAV and wound +IAV are denoted by #, wound and wound +IAV are denoted by *.