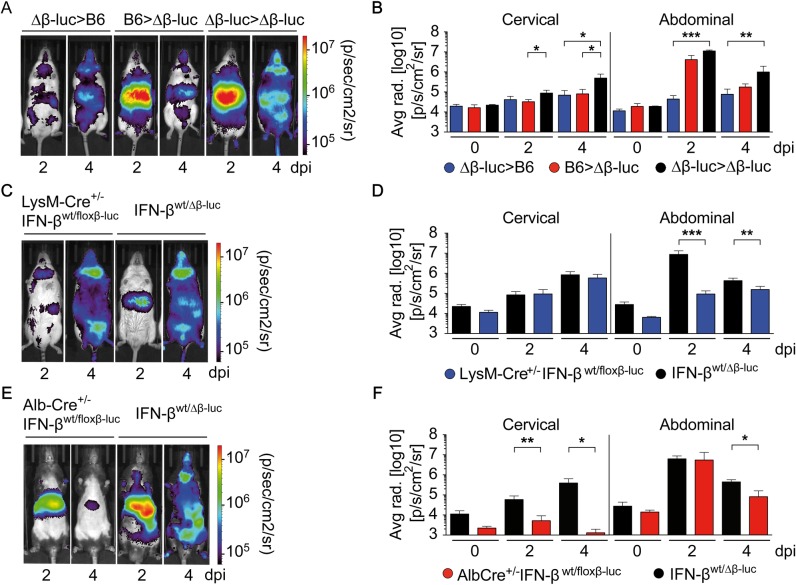
Fig 2. Upon CVB3 infection IFN-β induction in the liver is conferred primarily by hepatocytes.
(A and B) Lethally irradiated IFN-βwt/Δβ-luc (Δβ-luc) or C57BL/6 (B6) recipients were reconstituted with 1 x 107 BM cells from C57BL/6 (B6>Δβ-luc, red) or IFN-βwt/Δβ-luc mice (Δβ-luc>B6, blue), respectively. IFN-βwt/Δβ-luc recipients reconstituted with IFN-βwt/Δβ-luc BM were used as controls (Δβ-luc> Δβ-luc, black). Eight weeks after transplantation, mice were infected i.p. with 2 × 104 PFU CVB3 and imaged at 0, 2, or 4 dpi (n = 3–9). (A) One representative mouse of each group is shown. (B) Quantification of in vivo imaging by analysis of cervical and upper abdominal regions of interest (ROI). Values are mean + SD. (C-F) Conditional IFN-β reporter mice with an activated reporter in myeloid cells (LysM-Cre+/-IFN-βwt/floxβ-luc) or in hepatocytes (Alb-Cre+/-IFN-βwt/floxβ-luc) were infected as in (A) and imaged at the indicated dpi. IFN-βwt/Δβ-luc control mice with C57BL/6 albino or C57BL/6 background were used as controls, respectively. (C, E) One representative mouse of each genotype is shown. (D, F) Quantification of in vivo imaging (n = 3–9). Values are mean + SD. One-Way ANOVA test was used for statistical analysis, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.