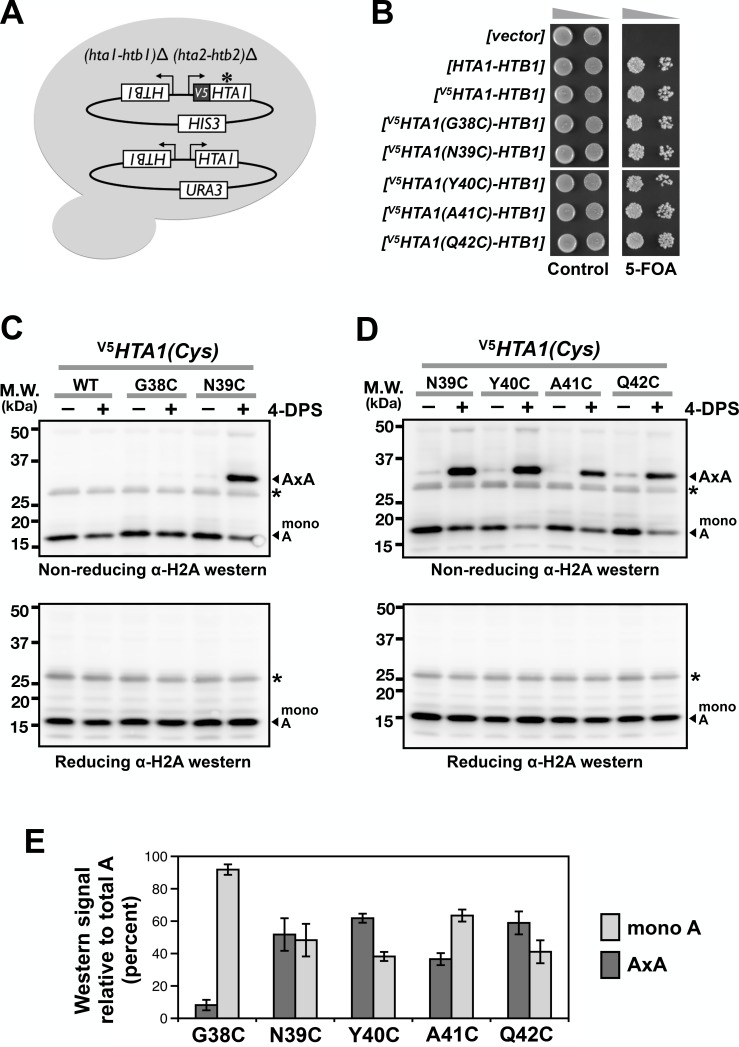
Figure 2. Cysteine substitution at multiple positions of the L1 region of H2A supports A-to-A crosslinking in yeast cells.
(A) The cartoon depicts the plasmid shuffle yeast system used to verify the functionality of the V5HTA1(Cys) mutants. (B) The ability of the HTA1(Cys) mutants to complement the lack of endogenous genes for H2A and H2B was indicated by growth in the presence of 5-FOA, which removes the wild type [HTA1-HTB1-URA3] vector from the cells. (C,D) VivosX analysis of yeast H2A was performed as described in Figure 1D except that the immunoblots were probed with an anti-H2A antibody (Active Motif). Asterisk (*) indicates a non-specific band. (E) Quantification of the AxA adducts and the uncrosslinked H2A (mono A) was performed as described in Figure 1F. Bars and error bars indicate the means and standard deviation of three biological replicates.