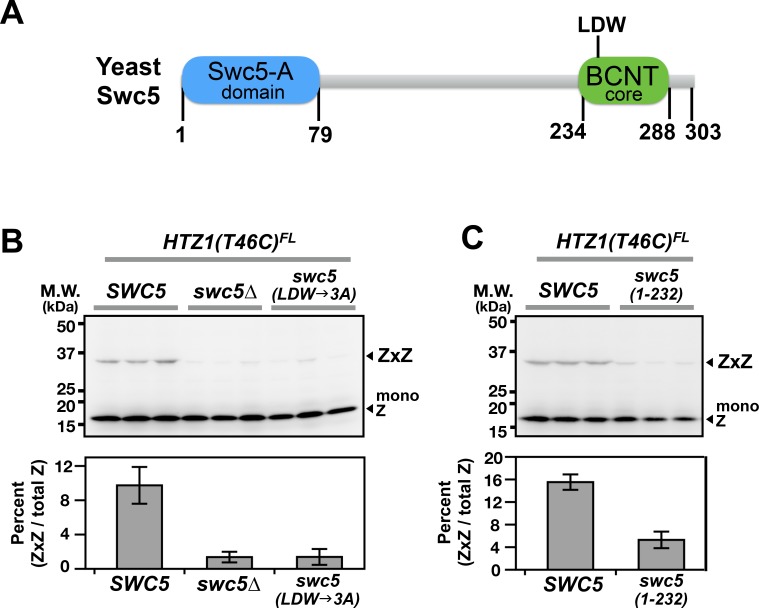
Figure 4. Domain analysis of Swc5 using H2A.Z VivosX.
(A) The cartoon depicts the domain organization of yeast Swc5 (Sun and Luk, 2017). (B,C) The yeast strain, HTZ1(T46C)FL swc5∆, was transformed by a single-copy plasmid containing either the wild-type SWC5 or the indicated SWC5 mutants or by the control vector (swc5∆). Top panels: Each strain was represented by three independent transformants and analyzed by VivosX in parallel. Htz1(T46C)FL and its crosslinked (ZxZ) adducts was detected by anti-FLAG immunoblotting. Bottom panels: Quantification of the immunoblots above. Bars and error bars represent the means and standard deviations of three biological replicates.