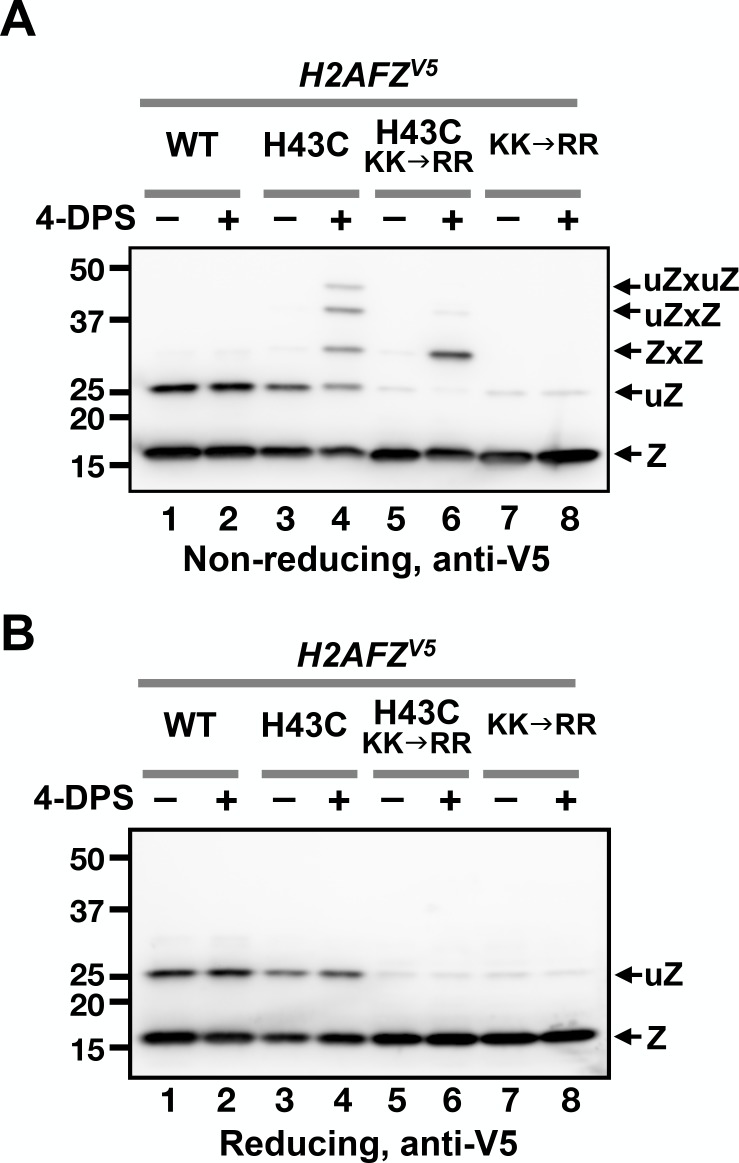
Figure 6. VivosX of H2A.Z in human cells.
(A, B) Human MCF10A cells expressing an ectopic H2AFZ(H43C)V5 gene was incubated with 4-DPS for 20 min before lysis using the TUNES buffer. Total lysates were resolved by non-reducing SDS-PAGE in (A) and reducing SDS-PAGE in (B) before analyzed by anti-V5 immunoblotting. Z: nonubiquitylated H2A.Z; uZ: monoubiquitylated H2A.Z; ZxZ: Z-to-Z crosslink adducts; uZxZ: crosslink adducts with one uZ and one Z; uZxuZ: crosslink adducts of two uZ molecules.