Figure 2. Neurosteroid synthetic pathway in the brain.
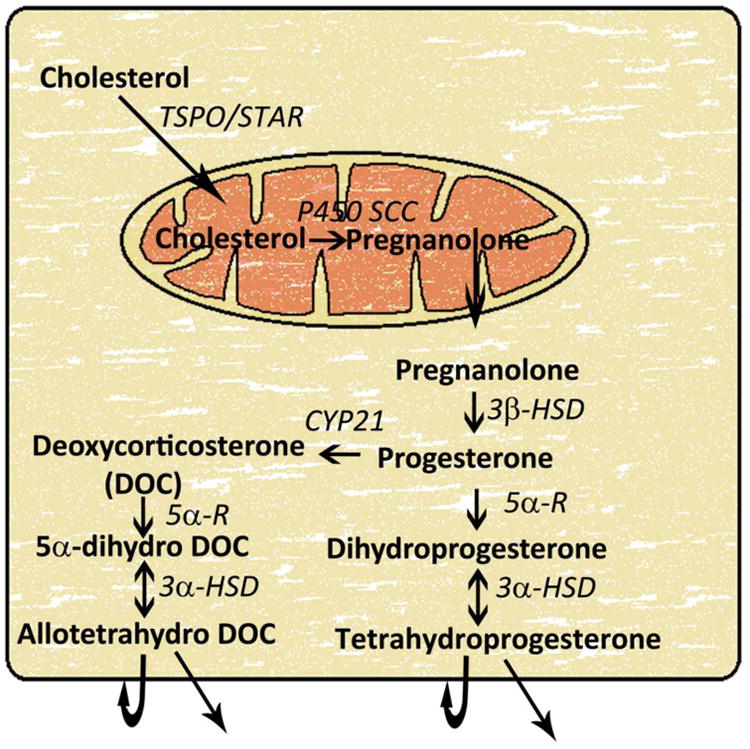
Cytoplasmic cholesterol is transferred to the inner mitochondrial membrane by steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR), also called translocator protein (TSPO), or peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. In the mitochondria, cholesterol is converted to pregnanolone by enzyme cytochrome P450 side-chain cleavage (P450scc) in a rate-limiting step. Pregnanolone is transferred back to the cytoplasm and gets converted to progesterone by enzyme 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD). Circulating progesterone can also enter the neurosteroid synthetic pathway at this step. Subsequently, progesterone is converted to dihydroprogesterone by the enzyme 5α-reducatse (5α-R) in the 2nd rate-limiting step in this biosynthetic pathway. Finally, dihydroprogesterone is converted to tetrahydroprogesterone (THP), also called allopregnanolone, by the enzyme 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3α-HSD). Progesterone can also be converted to deoxycorticosterone and then to allotetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone (THDOC). Both allopregnanolone and allotetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone can activate GABAA receptors expressed in the same cell or surrounding cells.
