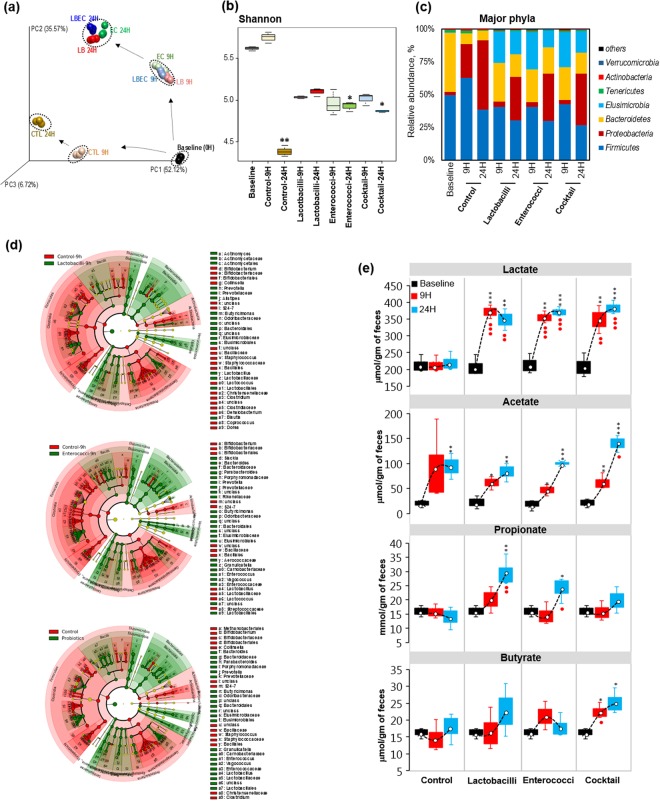
Figure 5.
Probiotic inoculation differentially changes the human fecal microbiome ex-vivo with increased production of SCFAs. (a) PCA analysis of human fecal microbiome showing beta-diversity upon treatment with lactobacilli, enterococci and probiotics cocktail after 9 and 24 h of anaerobic incubation in conditioned medium following the probiotic inoculation. (b,c) Shannon index (b) and major phyla changes upon lactobacilli, enterococci and cocktail treatment over the time up to 24 h. (d) Microbial cladogram indicating microbial clustering of human fecal microbiome in lactobacilli, enterococci and cocktail treated specimen compared to control specimen. (e) SCFAs including lactate, acetate, propionate and butyrate levels in human fecal microbiome after lactobacilli, enterococci and cocktail treatment up to 24 h. Values with *< 0.05, **0.01 and ***0.001 are significantly different within the same group compared to 0 h time point. Values with ● < 0.05, ●● < 0.01 are significantly different compared to controls at the same time points.