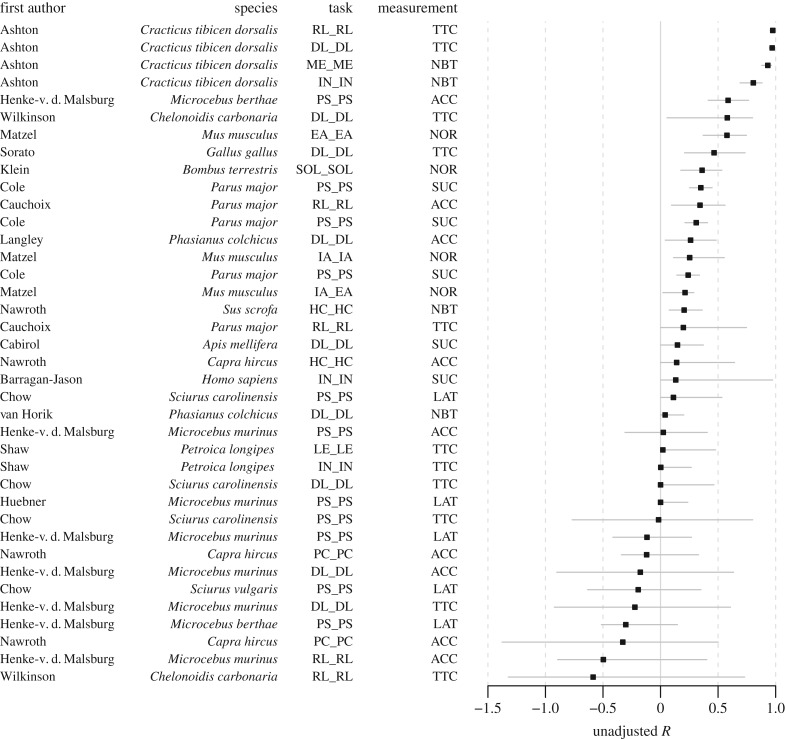
Figure 2.
Contextual repeatability R (unadjusted) and 95% bootstrapped confidence intervals for each dataset. Y-axis presents first author, species name, the type of cognitive task and the type of cognitive performance measurement. Cognitive measurement is used to quantify a cognitive process using accuracy such as proportion correct (ACC); the number of trials to reach a learning criterion (TTC); success-or-failure binary outcome (SUC); latency (LAT); normalized performance scores (NOR); the number of correct trials or errors over a fixed number of trials (NBT). The types of cognitive task include: mechanical problem solving (PS); discriminative learning (DL); reversal learning (RL); inhibition (IN); memory (ME); use of human cue (HC); external attention (EA); internal attention (IA); learning (LE); physical cognition (PC) that includes visual exclusion performance, auditory exclusion performance and object permanence; and spatial orientation learning (SOL).