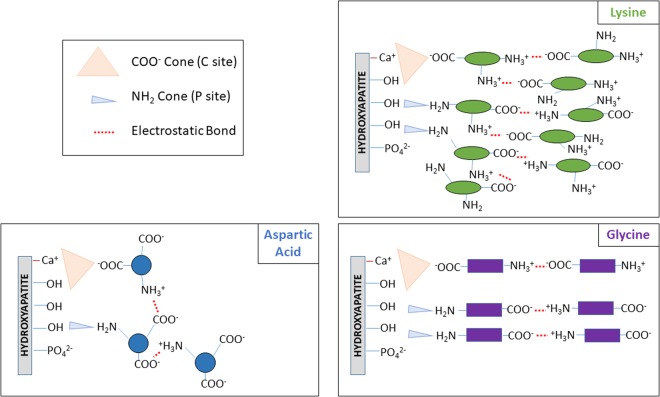
Figure 7.
A proposed schematic for the dominant mode of adsorption of the different amino acids at the ns-nHA surface. Both amine and carboxyl functional groups contributed to the attachment of the amino acids to the ns-nHA surface. This schematic generally encompasses each reaction condition, owing to little dependence observed on reaction condition (i.e. pH or pre-saturation with calcium); however, it is important to recognize that the fraction of amine groups which are ionized will change in the schematic as pH changes. Overall, the ease of approach towards the negatively charged ns-nHA surface is greatest for Lysine and Glycine, and more challenging for the negatively charged Aspartic acid. As a result, the attachment of Aspartic acid to the ns-nHA surface is more limited compared to the other two amino acids.