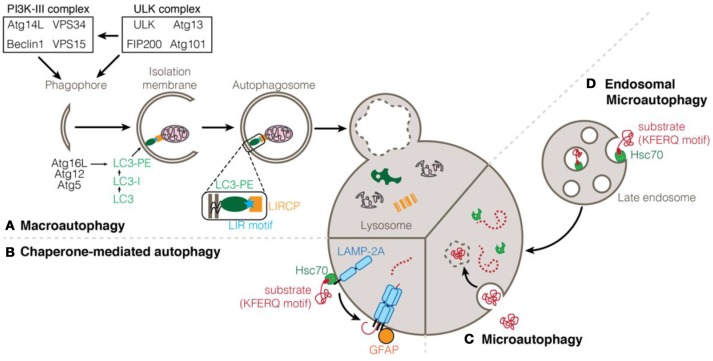
Figure 1.
Types of autophagy processes. (A) Macroautophagy is induced by the activation of the ULK1 and PI3K-III complexes. Modification of LC3/ATG8 proteins with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and anchorage to the membrane of the elongating autophagosome depends on the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16L conjugation system. LC3 can interact with cargoes and selective autophagy receptors via a LIR motif. Enclosed autophagosome eventually fuses with the lysosome for the degradation and recycling of its content. (B) Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) consists in the translocation of proteins into the lysosome through pores formed of LAMP-2A protein stabilized by phosphorylated GFAP. (C) Microautophagy consists in the internalization on cytoplasmic components into the lysosome by direct invagination of the lysosomal membrane. (D) Endosomal-microautophagy depends on the isolation of cytosolic protein in the late endosome before being addressed to the lysosome for degradation. Both CMA and endosomal-microautophagy rely on the chaperone protein Hsc70 that can bind to substrate proteins containing a KFERQ motif.