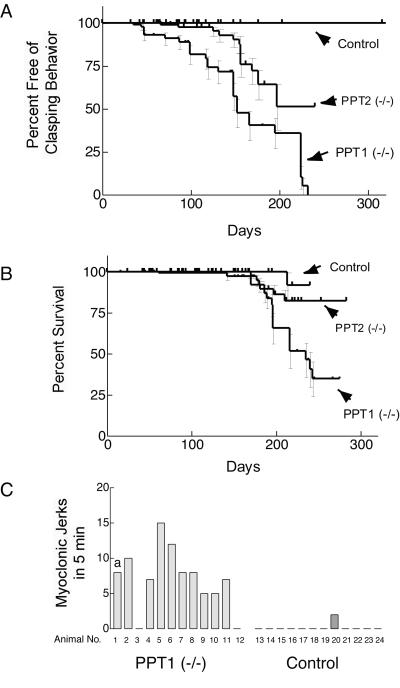
Figure 3.
Neurological abnormalities and decreased survival in PPT1 and PPT2 knockout mice. (A) Kaplan–Meier analysis of clasping abnormality in control, PPT1-deficient, and PPT2-deficient mice (n = 58, 70, and 96, respectively). The curves are significantly different from each other at a level of P < 0.0001 (two-tailed Mantel–Haenszel log rank test). (B) Kaplan–Meier survival curve of control, PPT1-deficient, and PPT2-deficient mice (n = 72, 129, and 160, respectively). Survival curves were statistically different from each other (P < 0.01). (C) Myoclonus in PPT1 knockout mice. Twelve PPT1 (−/−) and 12 wild-type mice at 6 mo of age were observed individually for a 5-min period and the number of myoclonic jerks was recorded. a, A spontaneous generalized tonic-clonic seizure lasting 1 min occurred in one control mouse during the 5-min observation period.