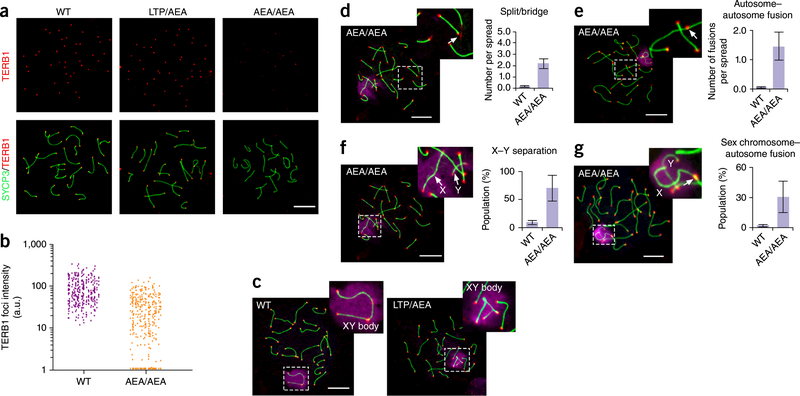
Figure 5.
The 647aea649 mutation of TERB1 results in telomere localization defect of TERB1, autosomal telomere aberrance and unpaired X and Y chromosomes, (a) Localization of TERB1 (red) and SYCP3 (green) on pachytene spermatocyte spreads from WT and Terb1AEAJAEA testes. Scale bar, 10 μm. (b) Quantification of the intensity of TERB1 foci at chromosome termini. More than ten spermatocyte spreads were used for quantification for each mouse, a.u., arbitrary units. Results are representative of three independent experiments with 6-week-old littermates. One male mouse of each genotype from the same litter was used in each experiment. (c) Representative mid-pachytene spermatocyte spreads from WT and heterozygous mice stained for SYCP3 (green), telomere (teIC, red) and γ-Η2ΑΧ (purple). Scale bar, 10 μm. (d-g) Representative images showing chromosome structural abnormalities in Terb1AEAJAEA mid-pachytene spermatocyte spreads: telomere splitting and bridging on autosomes (d), autosome-autosome telomere fusions (e), X-Y separation (f), and sex chromosome-autosome telomere fusions (g). Three independent experiments with different sets of mouse littermates were performed with similar results. One male mouse of each genotype from the same litter was used in each experiment. More than 50 spreads were counted for each mouse. Scale bars, 10 μm. Graphs show quantification of structural abnormalities as mean and s.d. of n = 3 independent experiments.