Figure 6.
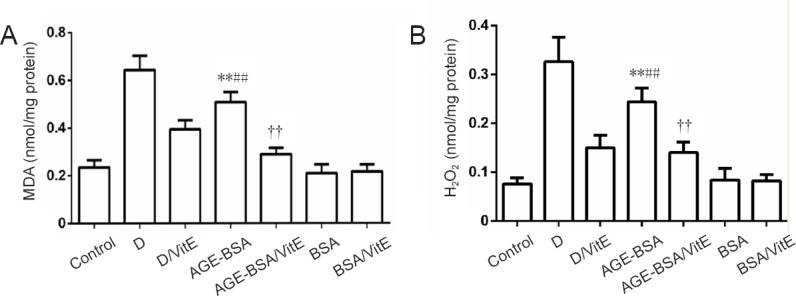
MDA and H2O2 levels in AGE-BSA and control mice with different treatments.
For MDA (A) and H2O2 (B) assays, **P < 0.01, vs. BSA group; ##P < 0.01, vs. AGE-BSA/VitE group; ††P < 0.01, vs. control group. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6; one-way analysis of variance followed by least significant difference test). Control group: Female mice were fed with normal commercial food. D: Diabetes was induced in female mice. D/VitE group: Diabetic female mice were fed with 0.125% (w/w) VitE at day 0.5 of gestation. AGE-BSA: Female mice were fed with commercial food containing 3% AGE-BSA. AGE-BSA/VitE group: Female mice were fed with 3% AGE-BSA for 4 weeks and then with 0.125% (w/w) VitE at day 0.5 of gestation. BSA group: Female mice were fed with commercial food containing 3% BSA. BSA/VitE group: Female mice were fed with 3% BSA for 4 weeks and then with 0.125% (w/w) VitE at day 0.5 of gestation. AGEs: Advanced glycation end products; BSA: bovine serum albumin; AGE-BSA: advanced glycation end product bovine serum albumin; VitE: vitamin E; MDA: malondialdehyde.
