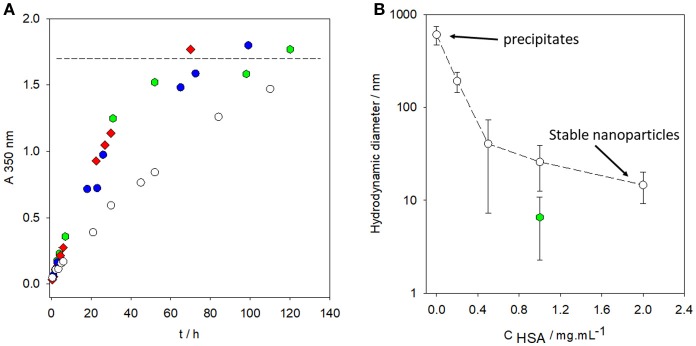
Figure 4.
(A) Absorbance at λ = 350 nm vs. time for dopamine solutions placed in oxidizing conditions (in the presence of O2 from the air and at pH = 8.5, 50 mM Tris buffer) in the absence of HSA ( ) and in the presence of HAS at various concentrations: 0.2 mg.mL−1 (
) and in the presence of HAS at various concentrations: 0.2 mg.mL−1 ( ), 1 mg.mL−1 (
), 1 mg.mL−1 ( ), and 2 mg.mL−1 (
), and 2 mg.mL−1 ( ). The horizontal dashed line corresponds to the saturation absorption at the end of the oxidation kinetics of dopamine. (B) Hydrodynamic diameter of PDA particles synthesized for 24 h from a 2 mg.mL−1 dopamine solution (50 mM Tris buffer at pH = 8.5) in the presence of HSA at different concentrations (
). The horizontal dashed line corresponds to the saturation absorption at the end of the oxidation kinetics of dopamine. (B) Hydrodynamic diameter of PDA particles synthesized for 24 h from a 2 mg.mL−1 dopamine solution (50 mM Tris buffer at pH = 8.5) in the presence of HSA at different concentrations ( ). Hydrodynamic diameter of PDA particles prepared in the same conditions as previously described and stored in a closed bottle (without refreshed air) for 3 months before characterization by dynamic light scattering (
). Hydrodynamic diameter of PDA particles prepared in the same conditions as previously described and stored in a closed bottle (without refreshed air) for 3 months before characterization by dynamic light scattering ( ). Reproduced from Chassepot and Ball (2014) with authorization.
). Reproduced from Chassepot and Ball (2014) with authorization.