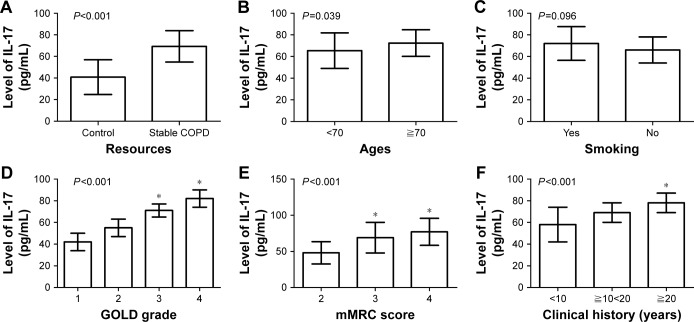
Figure 1.
Correlation between clinical factors and the serum level of IL-17 in patients with stable COPD.
Notes: (A) The expression of serum IL-17 was upregulated in patients with stable COPD compared with those in the control group (P<0.001). (B) Increased serum IL-17 level positively correlated with the age of patients (P=0.039). (C) Serum IL-17 expression did not correlate with the smoking status of patients (P=0.096). (D) The serum level of IL-17 in patients with GOLD-3 and -4 was higher than that in patients with GOLD-1 and -2 (*P<0.001). (E) Patients with mMRC scores of 3 and 4 showed higher serum levels of IL-17 compared with those with mMRC score of 2 (*P<0.001). (F) Patients with a long clinical history displayed a higher expression of serum IL-17 than those with a short history (*P<0.001).
Abbreviations: COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; GOLD, Global initiative for chronic obstructive Lung Disease; IL, interleukin; mMRC, modified British Medical Research Council.