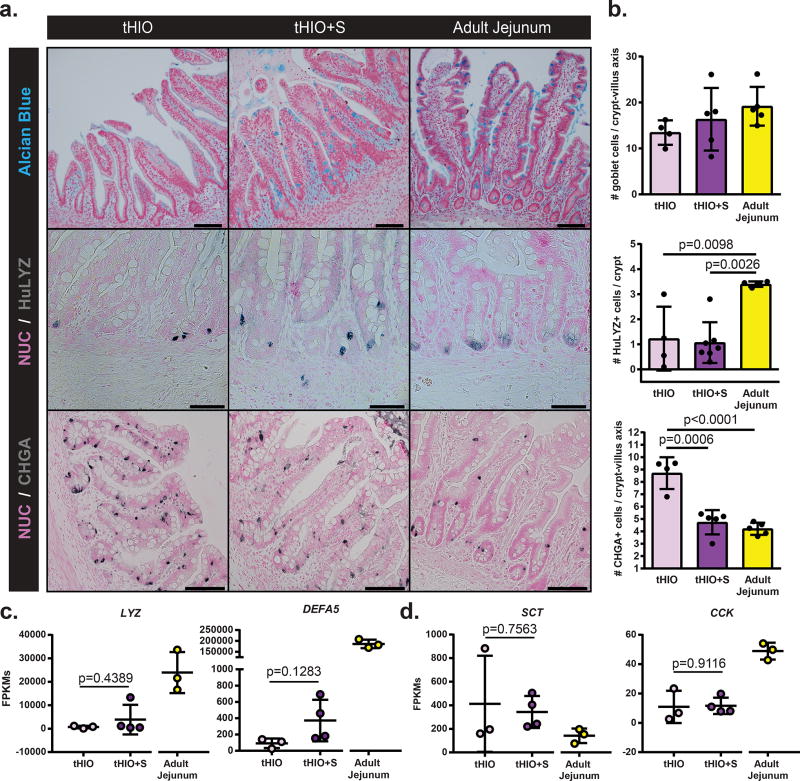
Figure 5. Strain’s impact on secretory lineages.
(a) Sections with staining for Goblet cells (alcian blue), Paneth cells (HuLYZ), and enteroendocrine cells (CHGA) in tHIO, tHIO+S and adult jejunum. Scale bar = 50 µm. These experiments were repeated three times independently and findings were similar. (b) Quantification of cell types in (a). No significant differences are observed in goblet cells, though the intensity of staining visually increases toward that of adult jejunum. The number of Paneth cells is reduced in HIOs compared to adult jejunum. The number of enteroendocrine cells followed a decreasing trend and was significantly less in tHIO+S than tHIO. Sample sizes are the following: tHIO n=4, tHIO+S n=5, and adult jejunum n=5. All samples are biologically independent. Data are represented as the mean ± SD. An ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc tests were performed and the statistical significance cutoff was p < 0.05. (c) Normalized FPKMs were plotted for tHIO, tHIO+S and adult jejunum for the Paneth cell produced antimicrobial peptides Lysozyme (LYZ) and Alpha-Defensin 5 (DEFA5). For both, expression follows an increasing trend in tHIO+S over tHIO, while much lower than that of adult jejunum, though not significant. (d) Normalized FPKMs were plotted for tHIO, tHIO+S and adult jejunum for enteroendocrine cell produced Serotonin (SCT) and Cholecystokinin (CCK). For (c,d) sample sizes are the following: tHIO n=3, tHIO+S n=4, and adult jejunum n=3. All samples are biologically independent. Data are represented as the mean ± SD. The unpaired student t test statistical significance cutoff was p < 0.05.