Fig. 3. Schematic diagrams (produced by MATLAB) of the three types of neural network topologies explored in this work, using four-layer networks as an example.
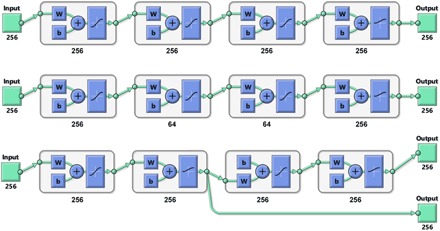
W block indicates multiplication by the weight matrix and b block indicates the addition of a bias vector. (Top) Fully connected full-width network. (Middle) Fully connected network with choke points. (Bottom) Functionally separated network with some layers explicitly dedicated to background rejection and others to interpretation—during the training process, the first output is the DEER form factor, and the second output is the distance probability density function.
