Figure 1.
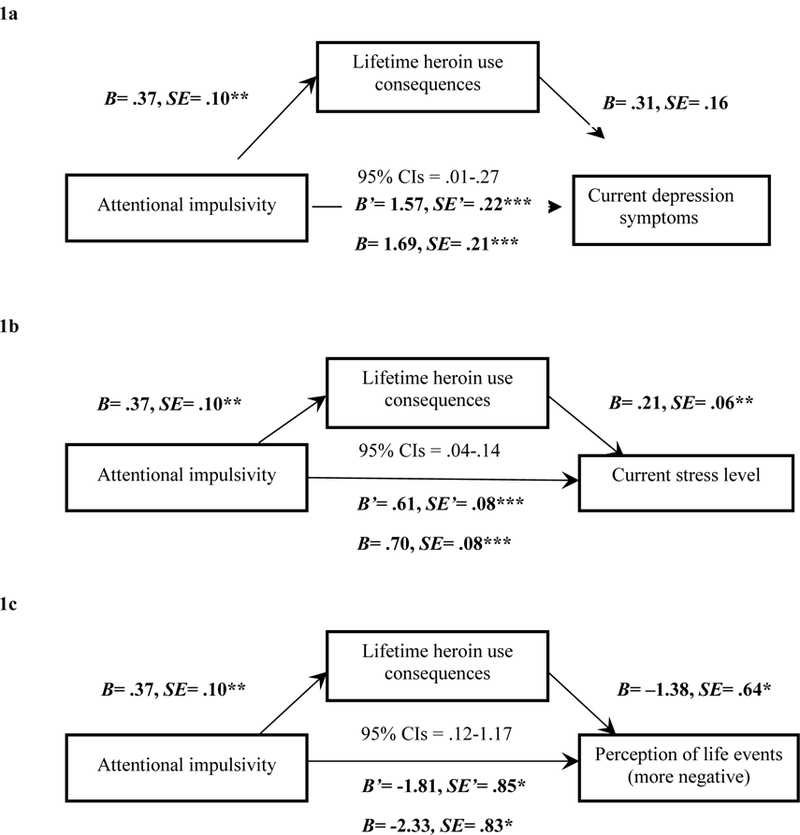
Mediation models with Attentional impulsivity (X), lifetime heroin-use consequences (M), and the parallel outcome measures (Y) of current depression symptoms (1a), stress level (1b), and perception of life events (1c). Note. *p<.05; **p<.01; ***p<.001. The unstandardized coefficients and standard errors shown account for the mediator in the equation. For each respective model, we list beta and standard error values for the mediation model’s direct effect (c’ path) and the unmediated model’s total effect (c path), as well as the 95% confidence interval range for the mediation model to demonstrate the indirect effect was different from zero and represented partial mediaiton.
