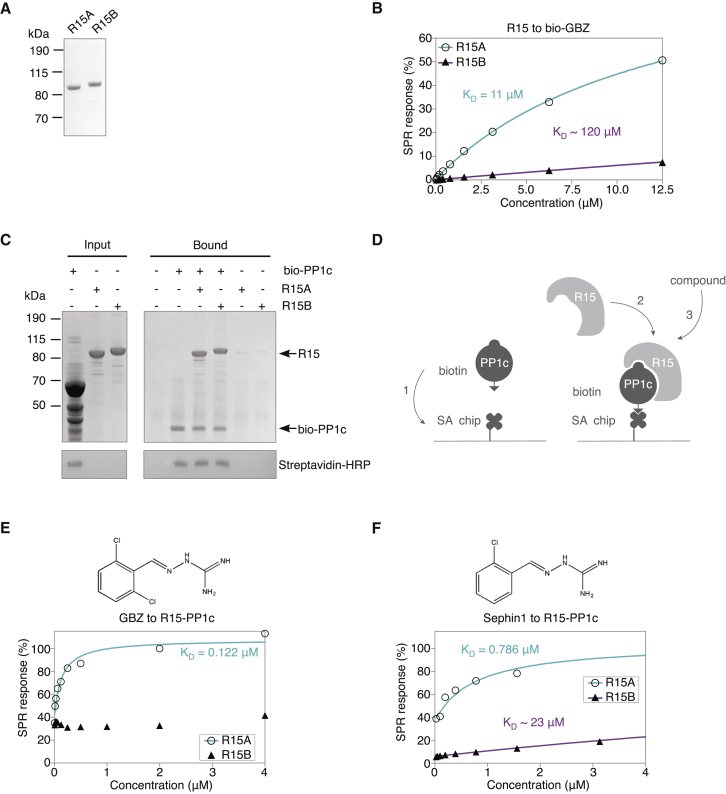
Figure 1.
An SPR-Based Assay with Reconstituted R15 Holophosphatases Measures Affinities of R15A Inhibitors
(A) Coomassie-stained gel showing recombinant proteins used in (B): MBP-R15A325-636-His and MBP-R15B340-698-His.
(B) Normalized steady-state binding curves from SPR showing binding of R15A (○ cyan) and R15B (▲ magenta) to bio-GBZ immobilized on the streptavidin sensor chip surface. Bio-GBZ (biotinylated GBZ) is an R15A inhibitor as potent as GBZ (Tsaytler et al., 2011).
(C) Coomassie-stained gel showing recombinant biotinylated PP1c (bio-PP1c; partially purified) and purified recombinant R15s (Input). Bio-PP1c, captured on neutravidin beads, bound R15A and R15B (Bound). Lower panel: immunoblot showing bio-PP1c.
(D) Cartoon depicting the reconstitution of R15 holophosphatases (R15A325-636-PP1c and R15B340-698-PP1c; see STAR Methods) on a streptavidin (SA) SPR chip.
(E and F) Normalized SPR steady-state binding curves showing binding of GBZ (E) or Sephin1 (F) to R15A-PP1c (○ cyan) and R15B-PP1c (▲ magenta) reconstituted on the streptavidin sensor chip surface.
Representative results of three independent experiments are shown.
See also Figures S1 and S2.