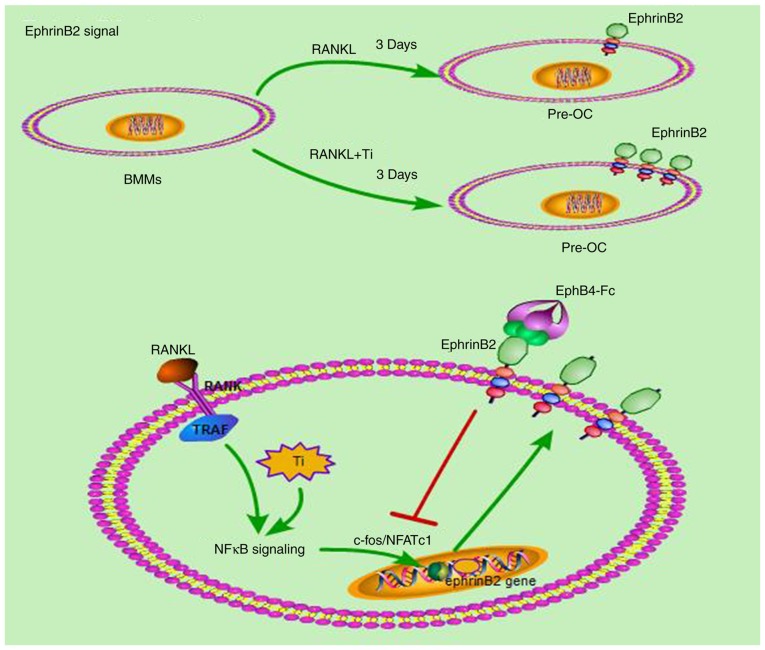
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram demonstrating that ephB4-Fc suppresses osteoclast formation and bone resorption induced by Ti particles. Ti particles activated the NFκB pathway in the presence of RANKL. A total of 3 days later, ephrinB2 expression increased significantly. By adding ephB4-Fc, ephrinB2 was activated, which inhibited the C-FOS/NFATc1 signaling pathway and inhibited the gene expression of cathepsin-K, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase and matrix metalloproteinase 9, by RANKL and Ti particles. Finally, ephB4-Fc inhibits osteoclasts differentiation and bone resorption by Ti particles. Ti, titanium; ephB4, erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular receptor 4; OC, osteoclast; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; RANK, receptor activator of NF-κB; RANKL, RANK ligand; TRAP, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase; C-FOS, Fos proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit; NFATc1, nuclear factor of activated T-cells 1.