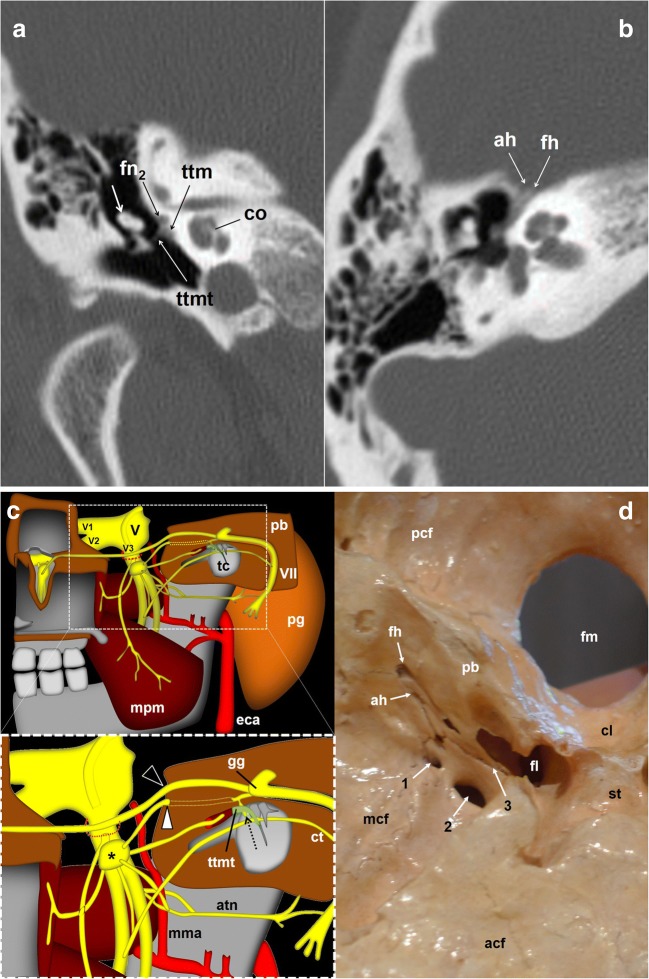
Fig. 6.
The glossopharyngeal nerve (gpn) and the tympanic nerve of Jacobson. a Skull base CT scan; coronal reconstruction of the right temporal bone, bone window. Once arriving at the tympanic cavity at the level of the promontory (p), the tympanic nerve forms a submucous plexus within the middle ear including the mastoid antrum and Eustachian tube. At the level of the tendon (ttmt) of the tensor tympani muscle (ttm), a branch of the tympanic plexus exits the cavity through a small duct and courses forward next to the facial nerve (fn2); short white arrow: malleus; co: cochlea. b Skull base axial CT scan; right temporal bone, bone window. The glossopharyngeal nerve fibres will exit the petrosal bone through the accessory hiatus (ah) after joining the lesser petrosal nerve of the facial nerve. fh: fallopian hiatus. c Schematic drawing of the right infratemporal fossa, view from inside. Glossopharyngeal nerve relationships with the facial (VII) and trigeminal (V) nerves. The lower drawing represents a detailed view of the region of interest (dashed rectangle). The deep great petrosal nerve (dotted arrow) comes up from the tympanic plexus at the level of the tendon of the tensor tympani muscle (ttmt) to merge with the lesser superficial pretrosal nerve coming from the geniculate ganglion (gg) of the facial nerve. The resulting nerve exits the petrosal bone (pb) to the middle cranial fossa at the level of the accessory hiatus (white arrowhead). The hiatus is located close and lateral to the fallopian hiatus (black arrowhead), through which the greater petrosal nerve enters into the skull. atn: auriculotemporal nerve; ct: chorda tympani; eca: external carotid artery; mpm: medial pterygoid muscle; mma: middle meningeal artery; pg: parotid gland; tc: tympanic cavity; V1: first trigeminal nerve branch; V2: second trigeminal nerve branch; V3: third trigeminal nerve branch; *Otic ganglion; dashed red circle: foramen ovale. d Skull base viewed from inside. The image shows the fallopian hiatus (fh) and the accessory hiatus (ah) on the right side, as well as the foramen spinosum (1), foramen ovale (2) and sphenopetrosal fissure (3), through which the lesser petrosal nerve that contains the glossopharyngeal nerve fibres may exit the cranium. acf: anterior cranial fossa; cl: clivus; fl: foramen lacerum; fm: foramen magnum; mcf: middle cranial fossa; pcf: posterior cranial fossa; st: sella turcica