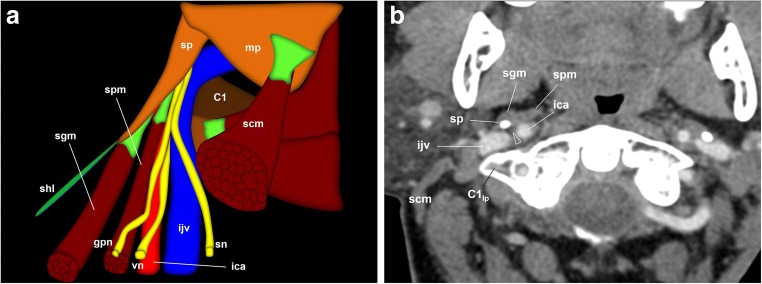
Fig. 8.
The glossopharyngeal nerve (gpn), cervical portion. a Schematic drawing of the glossopharyngeal nerve when leaving the left jugular foramen. The glossopharyngeal nerve is located medial to the internal jugular vein (ijv) and behind the internal carotid artery (ica) in the carotid space. The styloid process (sp) is the most lateral reference at this point. At the level of the first cervical vertebra (C1), the glossopharyngeal nerve surrounds the artery laterally and descends between the styloid process and stylopharyngeus muscle (spm). scm: sternocleidomastoid muscle; sgm: styloglossus muscle; shl: stylohyoid ligament; mp: mastoid process: sn: spinal nerve; vn: vagus nerve. b Axial contrast-enhanced CT scan of the neck, right side, at the level of the first cervical vertebra lateral process (C1lp); soft tissues window. At this point, the glossopharyngeal nerve (arrowhead) is located between the internal carotid artery anteriorly and the internal jugular vein behind. The styloid process is now in front of the glossopharyngeal nerve as it turns around the lateral side of the internal carotid artery to reach the dorsal aspect of the stylopharyngeus muscle. At this point, Hering’s nerve leaves the glossopharyngeal nerve to go down to the carotid body along the anterior aspect of the internal carotid artery