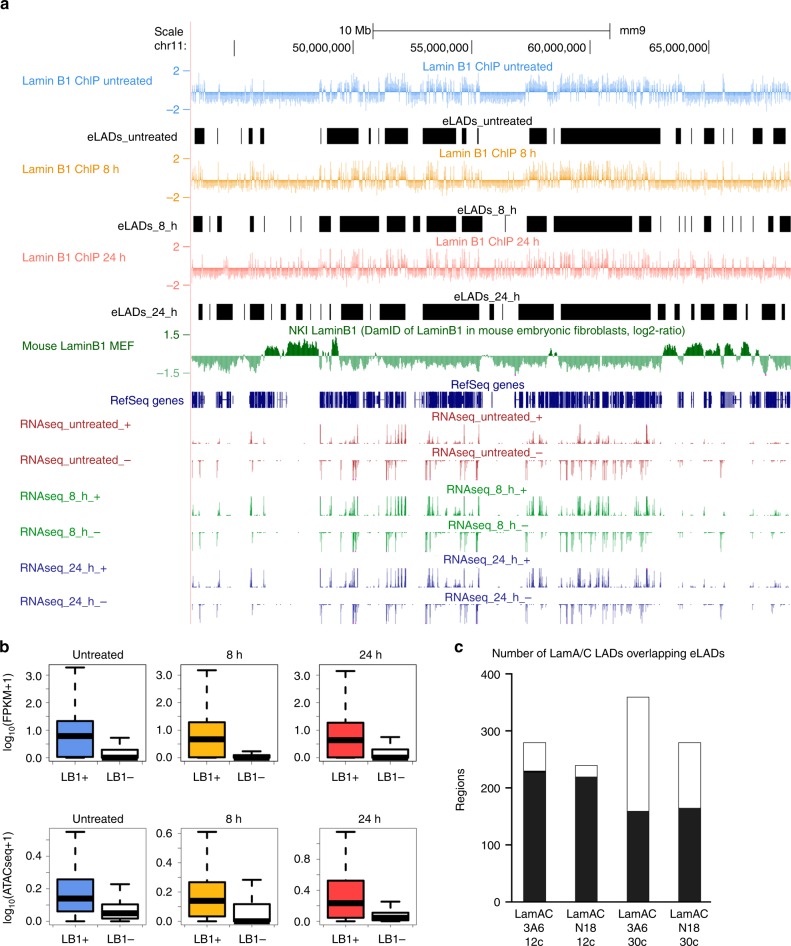
Fig. 3.
Definition of eLADs. a UCSC Genome Browser overview of one region across the chromosome 11 (mm9) containing the following information (from top to bottom): lamin B1 ChIP-seq profiles subtracting the IgG control in untreated NMuMG cells (blue) or in cells treated with TGF-β for 8 h (orange) or 24 h (red); eLADs identified in each condition (black); previously published LADs from mouse embryonic fibroblast cells (green); and RNA-seq strand-specific expression profiles at each time point (red for untreated NMuMG cells, green for cells treated with TGF-β for 8 h, and blue for cells treated for 24 h). b Gene expression within eLADs (given in FPKM) in NMuMG cells that were untreated (blue) or treated with TGF-β for 8 h (orange) or 24 h (red), as compared with the rest of genes (white) (left). Promoter ATAC-seq enrichment of lamin B1 + genes (measured in number of normalized reads) in NMuMG cells that were untreated (blue) or treated with TGF-β for 8 h (orange) or 24 h (red), as compared with the rest of genes (white) (right). Genes from eLADs were more likely to be expressed and located in accessible chromatin than other genes. The bottom and top fractions in the boxes represent the first and third quartiles, and the line, the median. Whiskers denote the interval between 1.5 times the interquartile range (IQR) and the median. c Bar plot showing the overlap between eLADs and lamin A/C LADs obtained after low or high sonication (12 cycles or 30 cycles, respectively) and with two different antibodies (3A6 and N18)