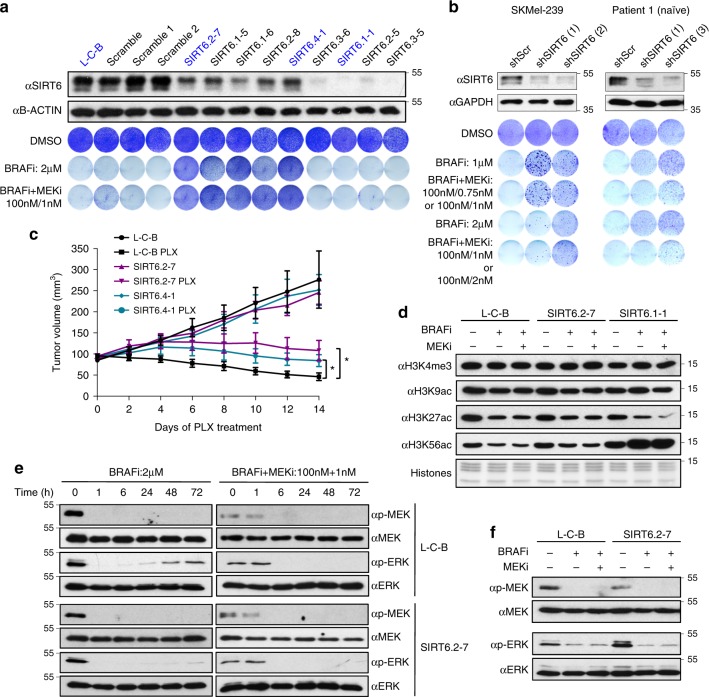
Fig. 2.
SIRT6 haploinsufficiency promotes resistance to MAPKi in BRAFV600E melanoma cells. a Immunoblot of SIRT6 in the indicated whole-cell lysates of SKMel-239 clonal CRISPR cell lines. B-Actin was used as a loading control (top; CRISPR clones used for follow-up experiments are indicated in blue). SKMel-239 cells were seeded at the same density and cultured in DMSO (1 week) or in the presence of the MAPKi (2 weeks) as indicated (bottom). b Immunoblot of SIRT6 in the indicated whole-cell lysates in SKMel-239 (left) and Patient 1 treatment-naive STC (right). GAPDH was used as a loading control. SKMel-239 and Patient 1 cells infected with control shRNA (scrambled) or shRNAs against SIRT6 (1, 2, or 3) were seeded at the same density and cultured in DMSO (1 week) or in the presence of MAPKi (4 and 5 weeks, respectively). c Quantification of tumor volume in nude mice bearing xenograft tumors of L-C-B, SIRT6.2–7, or SIRT6.4–1 cells that were fed a control or vemurafenib (PLX)-containing diet. Mann–Whitney test was performed for comparison between the three groups of mice treated with PLX. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05. n = 6–7. d The effect of BRAFi or BRAFi + MEKi treatment on H3K4me3, H3K9ac, H3K27ac, and H3K56ac in the indicated CRISPR cell lines after 4 days of treatment ± 2 µM of BRAFi or 100 nM BRAFi + 1 nM MEKi. Histones used as a loading control. e The effects of BRAFi or BRAFi + MEKi treatment for the indicated periods of time on components of the MAPK signaling pathway in the indicated CRISPR cell lines. f Immunoblot of 2 µM of BRAFi or 100 nM BRAFi + 1 nM MEKi treatment for 4 days on components of the MAPK signaling pathway in L-C-B and SIRT6.2–7 cells