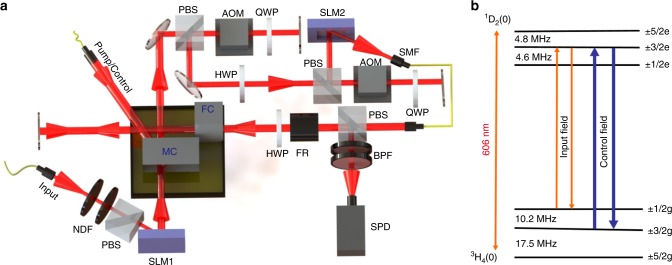
Fig. 1.
Experimental setup and atomic levels. a Schematic illustrations of the experiment. The AFC is prepared in a memory crystal (MC) and a narrow spectral filter has been prepared in a filter crystal (FC)49. The beam waist of the input light is 65 μm at the middle of the MC. The pump/control light has a beam waist of 300 μm inside the MC to ensure good overlap with the high-dimensional input light. The input pulses are attenuated to single-photon level by neutral density filters (NDF). The spatial modes of these photons are converted into OAM superposition states by a spatial light modulator (SLM1). After storage in the MC, the retrieved signal passes through two consecutive acousto-optical modulators (AOM)42, which act as a temporal gate and a frequency shifter. The AOM are used in double-pass configuration to ensure the photons’ spatial mode unchanged when the frequency of photons is swept over tens of MHz. The SLM2 and a single-mode fiber (SMF) are employed to analyze the OAM states of the retrieved photons. The FC is double-passed with help of a polarization beam splitter (PBS), a half-wave plate (HWP) and a Faraday rotator (FR). Two bandpass filters (BPF) centered at 606 nm are employed to further suppress noises before the final detection of signal photons using single-photon detector (SPD). QWP quarter-wave plate. b Hyperfine states of the first sublevels of the ground and the excited states of Pr3+ in Y2SiO5. The input field is resonant with 1/2g–3/2e, and the control field is resonant with 3/2g–3/2e (see Methods section for details)