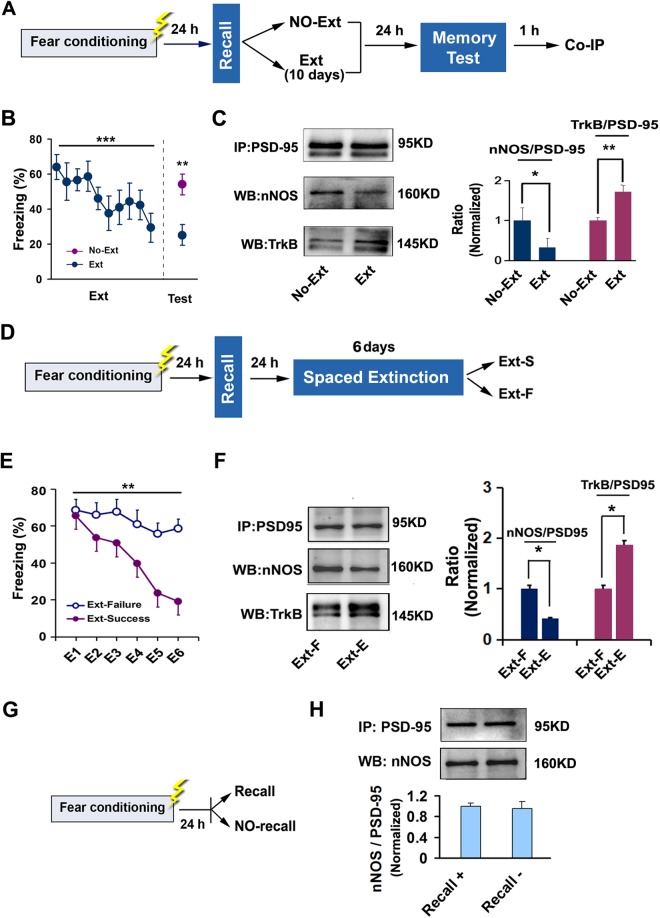
Figure 1.
Contextual fear extinction induces a shift from PSD-95-nNOS to PSD-95-TrkB coupling in the dorsal hippocampus. (A) Design of the experiments for (B–D). (B) Freezing behavior measured during extinction trial and retrieval of extinction memory (n = 6). (C) PSD-95-nNOS and PSD-95-TrkB complex levels in the dorsal hippocampus after contextual fear extinction. (PSD-95-nNOS: n = 5; PSD-95-TrkB: n = 5). (D) Design of the experiments for (E and F). (E) Freezing behavior measured during extinction trial from the mice with successful extinction and failured extinction (n = 5–6). (F) PSD-95-nNOS and PSD-95-TrkB complex level in the dorsal hippocampus after contextual fear extinction (PSD-95-nNOS: n = 5–6; PSD-95-TrkB: n = 5–6). (G) Design of the experiments for (H). (H) PSD-95-nNOS complex level in the dorsal hippocampus after recall (n = 3). Ext: extinction. Ext-S: extinction success. Ext-F: extinction failure.