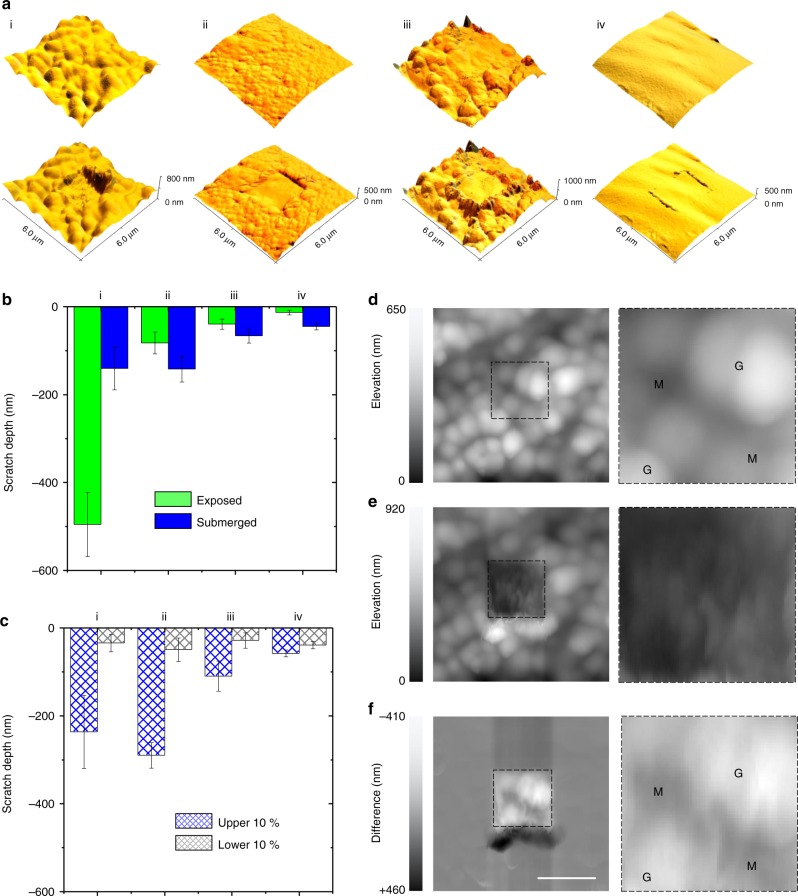
Fig. 2.
2D AFM scratch tests on the cuticle surfaces. All panels labeled with (i) represent M. galloprovincialis, (ii) M. californianus, (iii) S. bifurcatus, and (iv) M. capax. a Representative AFM topographic images of all mussel thread surfaces without (top) and with (bottom) scratch traces. b Scratch depths as a function of species and hydration. c The hydrated datasets are further partitioned in the upper and lower 10%. d–f A representative scratch test on a M. galloprovincialis thread (scale bar = 2 µm), with AFM height channel recordings prior (d) and after (e) damaging the surface, as well as a difference image of both (f). Zoom-ins of the region of interest are included on the right (M = matrix and G = granules) (Bars are mean ± s.e.m., n = four biological replicates)