Fig. 1.
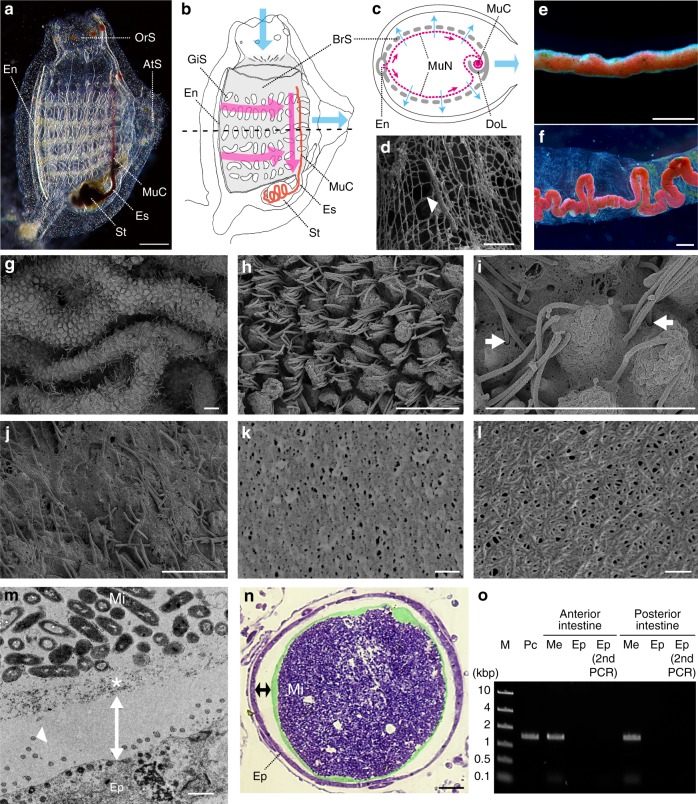
Gut barrier membrane of the tunicate Ciona intestinalis Type A. a–c The feeding mechanism of C. intestinalis Type A (a, juvenile specimen; b, anatomy; c, horizontal section at the dotted line in b). Cyan and magenta arrows denote the flows of seawater and mucus nets (MuN), respectively. While seawater, drawn from the oral siphon (OrS) into the branchial sac (BrS, gray), passes through the gill slits (GiS) to be expelled from the atrial siphon (AtS), particulate matter in seawater is trapped with mucus nets covering the inside of the branchial sac (magenta dotted lines in c). Mucus nets, secreted from the endostyle (En) and conveyed to the dorsal lamina (DoL), are rolled up as a single mucus cord (MuC, a red line in b), which is then transported posteriorly to the esophagus (Es) and the stomach (St). The mucus cord is recognizable due to trapped red beads. d An SEM image of rectangular mucus net and a trapped microbe (arrowhead). e A mucus cord isolated from the dorsal lamina. f Feces. A winding mucus cord is enveloped inside a transparent membrane. g–l The formation of envelope membranes (SEM images). g Intestinal mucosal surface with epithelial ridges. h The apical side of epithelial cells projects into the luminal space, and cilia extend from spaces between projections. i The epithelial surface is covered with a membrane that cilia penetrate (arrows). j A delaminating membrane from the epithelium. Cilia, but not projections, are recognizable. k The porous surface of a delaminated membrane. l The chemically purified framework of a membrane: meshed nanofibers. m, n Cross-sections showing axenic spaces (double-headed arrows) over the gut epithelium (Ep) (m, TEM; n, light microscopy). Intestinal microbes (Mi) are confined to the luminal space by multi-layered membranes (* or false-colored green). An arrowhead indicates one of the cilium sections. o Confirmation of the axenic condition by PCR amplifications of 16S rRNA genes. M, markers; Pc, positive control (food microbes); Me, isolated membranes enclosing food residues. Scale bars a 200 μm; d, m 1 μm; e, f, 500 μm; g–j, 5 μm; k, l 100 nm, and n 8 μm