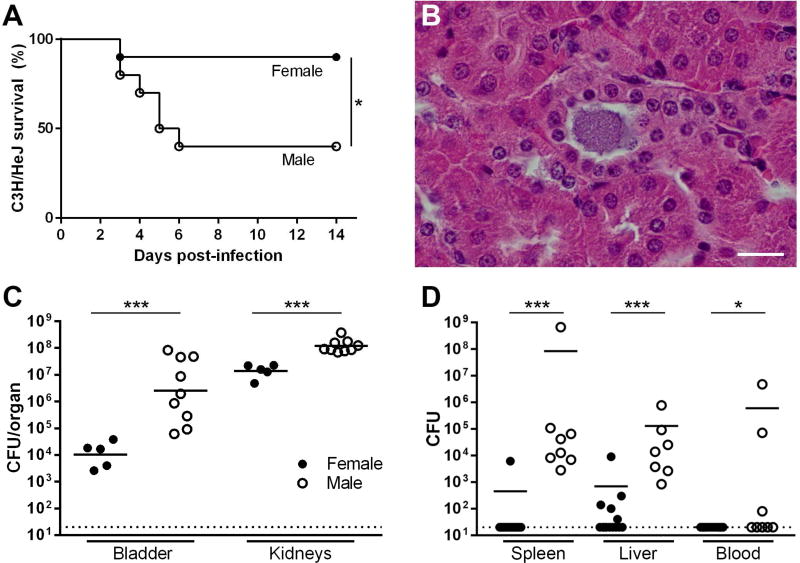
Figure 7. UPEC-infected TLR4-deficient males fail to form renal abscesses and are vulnerable to lethal dissemination.
(A) Neutrophil recruitment and abscess formation were necessary for containment of infection; when the TLR4-deficient C3H/HeJ strain was used, male mice were much more likely to succumb to infection (n=10 per group, *P=0.0274), an outcome not seen in immunocompetent C3H/HeN mice. Surviving C3H/HeJ males failed to form abscesses surrounding UPEC-infected tubules (B; scale bar, 20 µm). Male C3H/HeJ developed significantly higher bladder and kidney titers than females 3 dpi (C, ***P=0.001). In addition, male C3H/HeJ mice were significantly more susceptible than females to dissemination, the likely cause of death, as evidenced by bacterial loads 3 dpi in spleen, liver and blood (D, ***P<0.001, *P<0.05). Dotted lines indicate limit of detection.