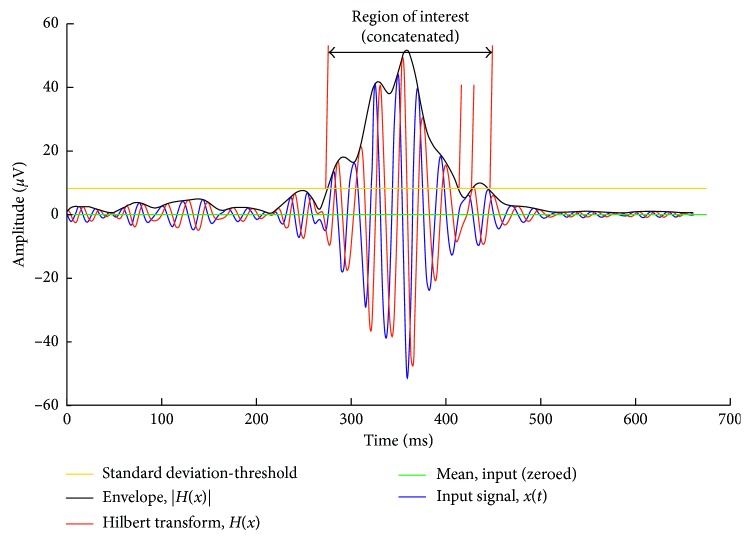
Figure 1.
Definition of region of interest according to Burnos et al. [64]. The signal is high-pass filtered (finite impulse response, Blackman windowed sinc) with a cutoff frequency of 80 Hz. A Hilbert transform of the filtered signal (blue) yields a complex output with a 90-degree phase-shifted imaginary part (red). The absolute value of the Hilbert transform is used to generate the signal's envelope (black). The standard deviation of the signal's envelope is the baseline for deriving the threshold for delimiting regions of interest as a first step. As depicted in the figure, closely neighbouring regions are concatenated to form a single one.