Figure 4.
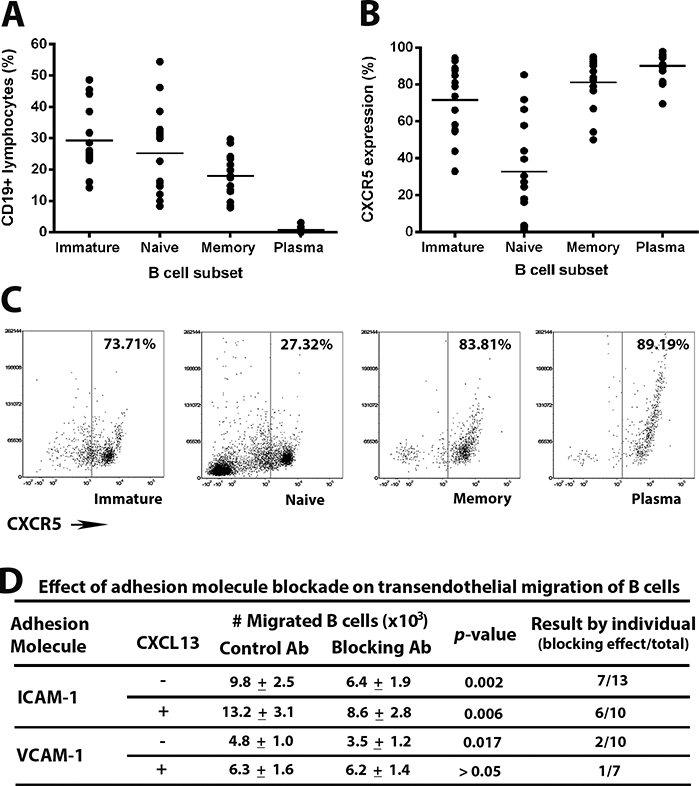
[A-C] Expression of CXCR5 on human peripheral blood B cells of adult human subjects. CD19+ B cells, enriched from peripheral blood leukocytes by negative selection, were classified as immature, naïve, memory and plasma cells on the basis of CD20, CD27 and CD38 expression [A], and percentage of cells expressing CXCR5 was determined for each subset [B]. Circles represent results for individual subjects and crossbars represent mean. Flow dot plots present CXCR5 expression on B cell subsets from one representative human subject [C]. [D] Effect of antibody (Ab)-mediated adhesion molecule blockade on human B cell migration across simulated retinal endothelium, as described in the Figure 1 legend. Migration was studied without or with CXCL13 added to the lower chambers of transwells. Number of migrated B cells is expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean, and compared by one-tailed paired Student’s t-test for each set of conditions. Effect of blockade for individual human subjects is presented separately, as number of subjects whose B cells migrated in significantly reduced numbers in the presence of adhesion molecule blockade, over total number of human subjects.
