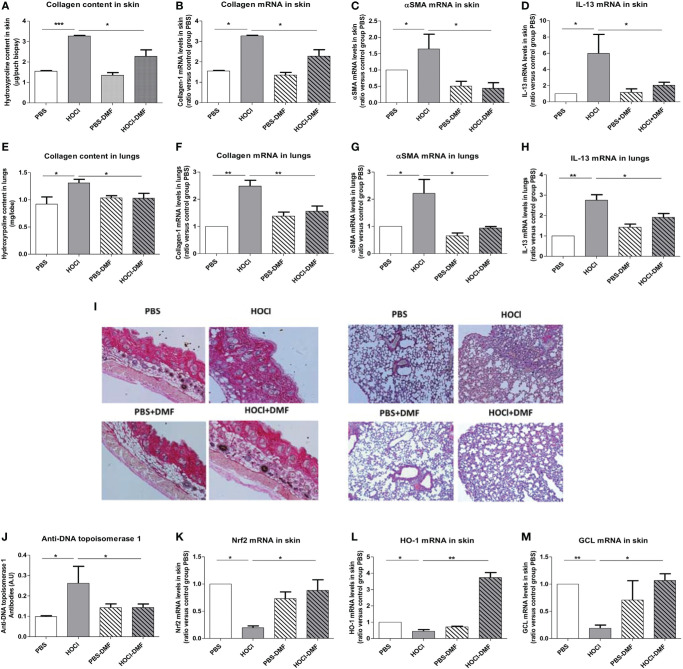
Figure 6.
Effects of in vivo treatment with DMF on HOCl-induced SSc. BALB/c mice were intradermally injected with HOCl or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and simultaneously treated with DMF or vehicle alone for 6 weeks. (A–D) In vivo treatment with DMF reduces skin fibrosis in mice with HOCl-induced SSc. (A) Collagen type I content in skin (Hydroxyproline, mg/punch biopsy). (B) Collagen type I mRNA levels in skin (ratio versus control group PBS). (C) Alpha-SMA mRNA levels in skin (ratio versus control group PBS). (D) IL-13 mRNA levels in skin (ratio versus control group PBS). (E–H) DMF reduces lung fibrosis in mice with HOCl-induced SSc. (E) Collagen type I content in lungs (Hydroxyproline, mg/lobe). (F) Collagen type I mRNA levels in lungs (ratio versus control group PBS). (G) Alpha-SMA mRNA levels in lungs (ratio versus control group PBS). (H) IL-13 mRNA levels in lungs (ratio versus control group PBS). (I) Skin and lung biopsies stained with Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Representative sections of 5 µm. Photographs were taken with a Nikon Eclipse 80i microscope. Original magnification ×50. (J) Anti-DNA topoisomerase 1 antibodies levels in the sera (A.U). (K–M) In vivo treatment with DMF upregulates the Nrf2 pathway in the skin. Levels of Nrf2 (K), HO-1 (L), and GCL (M) mRNAs in the skin (ratio versus control group PBS). Abbreviations: AU, arbitrary units; DMF, dimethyl fumarate; SSc, systemic sclerosis; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1. Values in (A–M) are mean ± SEM (n = 8 mice per group). *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001, by Mann–Whitney U test.