Fig. 3.
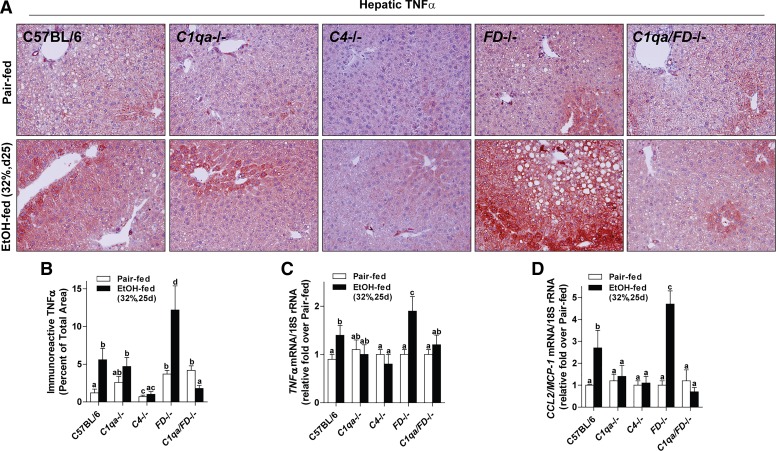
Complement component 1, Q subcomponent (C1q) and complement protein 4 (C4) contributed to, while complement factor D (FD) protected from, chronic ethanol (EtOH)-induced hepatic inflammation. Wild-type (WT), C1q-deficient (C1qa−/−), complement protein 4-deficient (C4−/−), complement factor D-deficient (FD−/−), and C1q/FD−/− were allowed free access to EtOH [32%, day (d) 25] or pair-fed control diets. A: paraffin-embedded liver sections were deparaffinized followed by immunodetection of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin. All images were acquired using a ×20 objective. B: TNF-α-stained areas were quantified from at least three images per slide using Image-Pro Plus software. Expression of TNF-α (C) and macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCR2, D) mRNA was detected in mouse livers using Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. Values with different alphabetical superscripts were significantly different from each other (P < 0.05). Values represent means ± SE; n = 4–8 pair-fed and 6–12 EtOH-fed mice.