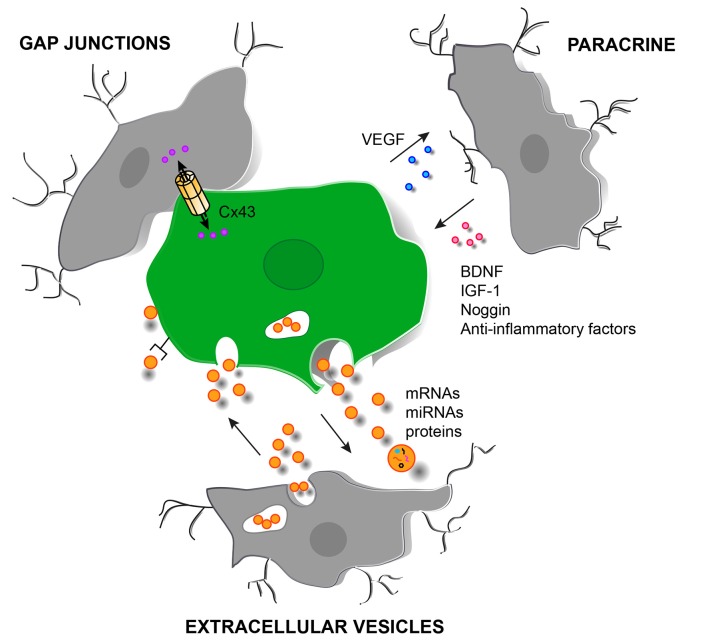
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of different cell signaling pathways involved in the interaction between grafted NPCs and host microglia in the injured brain. Paracrine signaling with the release of soluble factors from SVZ-derived NPCs (in green) and microglia (in gray). Direct molecule interchange mediated by gap junctional communication can also occur between microglia/macrophages and grafted NPCs. In addition, extracellular vesicles (orange circles) can be released by NPCs and by microglia with the possibility to deliver bioactive molecules such as mRNAs, miRNAs and proteins. The delivery can be carried out in different ways: (i) by endocytosis of the vesicle; (ii) by activation of surface receptors; and (iii) by membrane fusion or by a Cx43-dependent mechanism. Abbreviations: BDNF, brain derived-neurotrophic factor; Cx43, connexin 43; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.