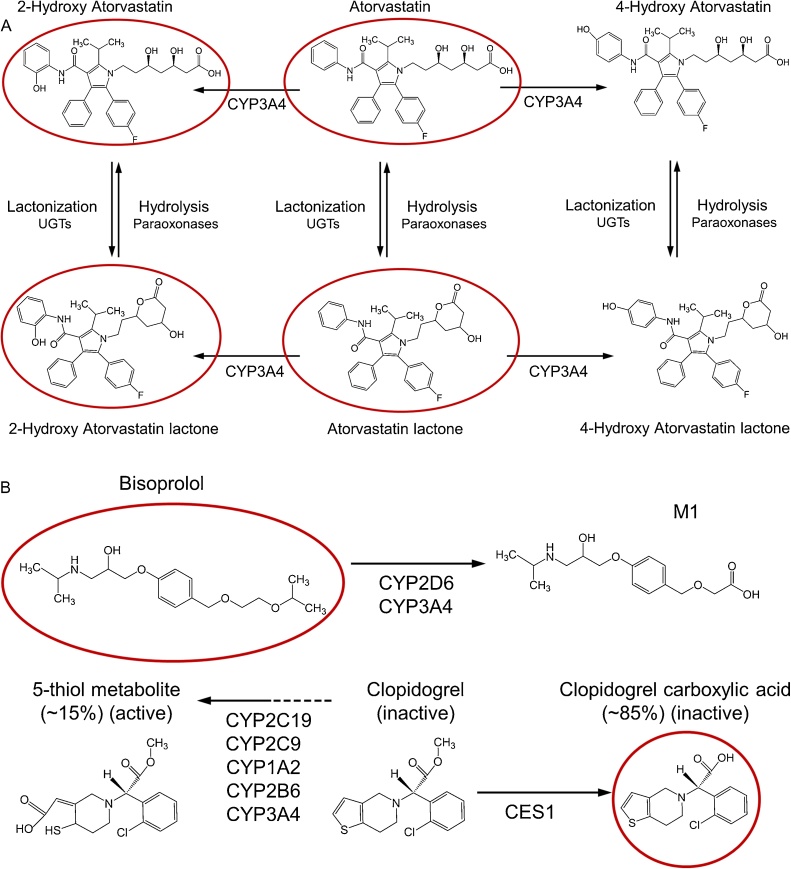
Fig. 1.
Chemical structures and relevant metabolism of analytes.
Abbreviations: CES1 = carboxylesterase 1; CYP = cytochrome P450; UGTs = uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases. The red rings denote the analytes quantified in this assay: parent ATV, its major hydroxylated metabolite (2-OH ATV), their corresponding lactones (ATV L and 2-OH ATV L), BSP, and the major CLP metabolite, CLP–CA. A: ATV and its hydroxylated acid metabolites, 2-OH ATV and 4-OH ATV, actively inhibit HMGCR to reduce circulating low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, although 2-OH ATV is the more abundant active metabolite [6]. The lactone metabolites are produced from the acid forms of ATV by UGTs, do not inhibit HMGCR, but are implicated in statin-induced muscle toxicity [[11], [12], [13]]. B: BSP is a cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist racemate; ∼50% is renally excreted unchanged and ∼50% undergoes hepatic metabolism into labile or inactive metabolites prior to predominant renal excretion [14,15]. The inactive M1 metabolite of BSP is the most abundant BSP metabolite in human urine [15]. The active metabolite of CLP irreversibly inhibits platelet P2Y12 receptors, but is highly labile. Nevertheless, ∼85% of administered CLP is metabolised to the readily quantifiable inactive circulating metabolite, CLP-CA, which has been correlated with platelet inhibition indices [18], CLP non-adherence and variable metabolism [18,19].