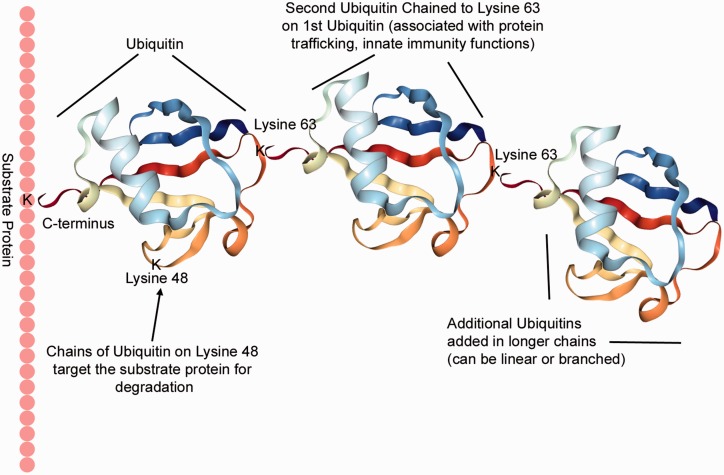
Fig. 1.
Ubiquitination is binding of the 76 amino acid protein ubiquitin, usually to a lysine residue of a target/substrate protein. Additional ubiquitin molecules attach to the original ubiquitin, with the C-terminus of the new ubiquitin binding to specific lysine residues of the earlier ubiquitins. Functional consequences of ubiquitination depend on the types of chains formed. A chain of at least four ubiquitins connected through Lysine 48 target the substrate for ubiquitination; linear and branched chains through M1, K6, K11, K27, K29, K33, K48, or K63 are all possible. Ubiquitin folding picture produced by NGL Viewer.9