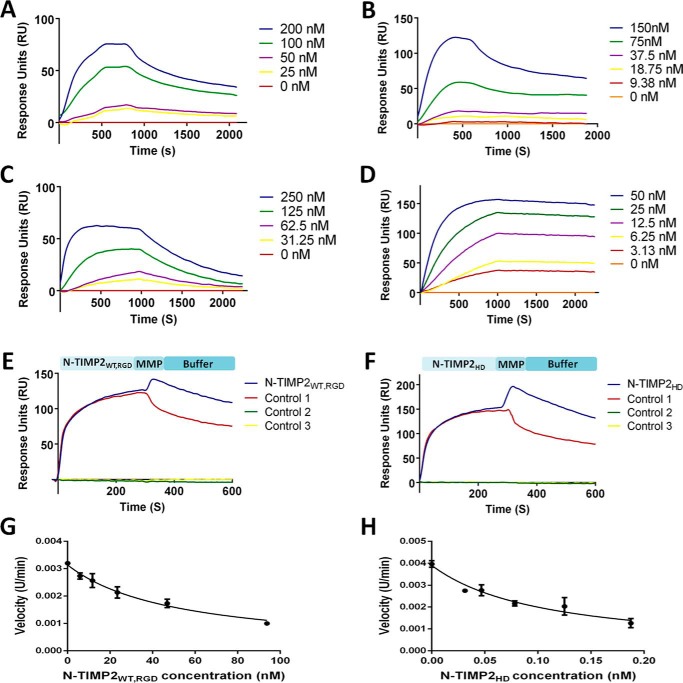
Figure 2.
SPR sensorgrams and the inhibitory activity of the N-TIMP2WT, RGD and N-TIMP2HD variants. N-TIMP2WT, RGD (A) and N-TIMP2HD (B) binding to integrin αvβ3 is shown. N-TIMP2WT, RGD (C) and N-TIMP2HD (D) binding to MMP-14CAT is shown. Dual binding of N-TIMP2WT, RGD (E) and N-TIMP2HD (F) to integrin αvβ3 and MMP-14CAT is shown. E and F, variants were allowed to flow over integrin αvβ3 immobilized on the chip, followed by MMP-14CAT (blue) or buffer (control 1, red) injection at 300 s. There was an increase in response units (RU) for the variants after MMP-14CAT injection, which indicates that these variants bind simultaneously to both receptors. In control 2 (green), a buffer was allowed to flow over the integrin αvβ3 immobilized chip, followed by MMP-14 injection at 300 s. In control 3 (yellow), a buffer was allowed to flow over the integrin αvβ3 immobilized chip throughout the entire experiment. Substrate degradation velocity at different concentrations of N-TIMP2WT, RGD (0–100 nm) (G) and N-TIMP2HD (0–0.2 nm) (H) were fitted to Morrison's equation (Equation 2) to obtain Ki values.