Figure 1.
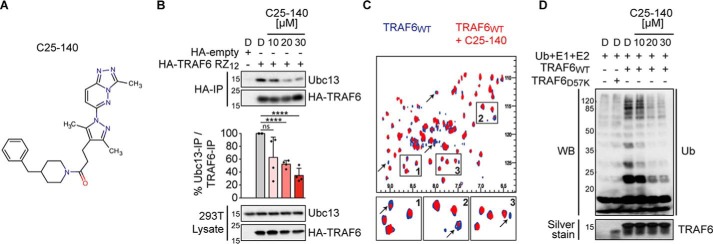
C25-140 binds TRAF6, inhibits TRAF6–Ubc13 interaction and TRAF6 activity. A, chemical structure of C25-140. B, ectopically expressed HA-TRAF6 RZ12 in HEK293T cells co-immunoprecipitates less endogenous Ubc13 after C25-140 treatment. Ubc13 levels in the IP fractions were densitometrically quantified in relation to precipitated TRAF6. Error bars, S.D.; n = 4 biological replicates were quantified; unpaired t test (two-tailed); ****, p < 0.0001; D, DMSO. C, heteronuclear correlation NMR experiments using 15N-labeled WT TRAF6 RZ1 either alone (blue) or in the presence of C25-140 (red; molar ratio of TRAF6/C25-140 = 1:5). Several NMR signals undergo intensity reduction or broadening beyond detection (arrows), indicating binding in the so-called “intermediate exchange regime.” This suggests that protein–compound complex lifetime is in millisecond time scales and confirms direct binding of the compound to TRAF6. D, C25-140 dose-dependently counteracts in vitro ubiquitination by untagged WT TRAF6 RZ1 together with the E2 complex Ubc13–Uev1a. WB, Western blotting.